DataHub on EKS
Introduction
DataHub is an open source data catalog that enables end-to-end data discovery, data observability, and data governance. This extensive metadata platform allows users to collect, store, and explore metadata from various sources, such as databases, data lakes, streaming platforms, and ML feature stores. DataHub provides many features, a rich UI for searching and browsing metadata, as well as an API for integrating with other applications.
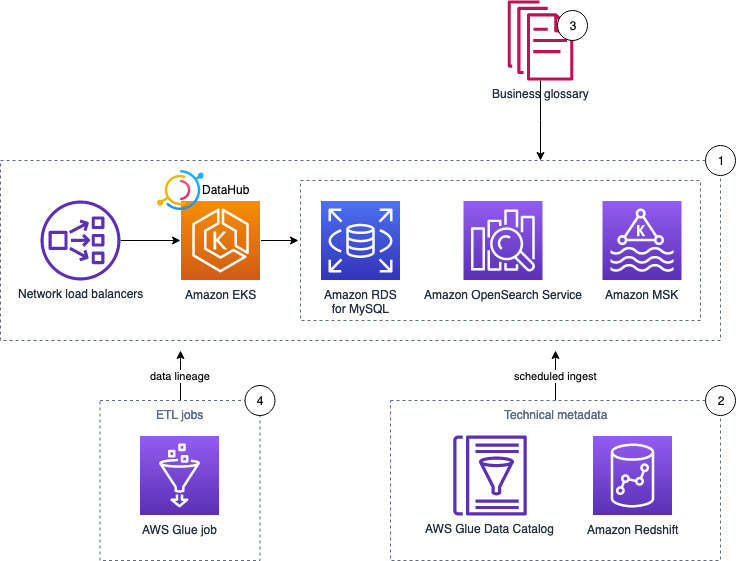
This blueprint deploys DataHub on an EKS cluster, using Amazon OpenSearch Service, Amazon Managed Streaming for Apache Kafka (Amazon MSK), and Amazon RDS for MySQL as the storage layer for the underlying data model and indexes.
DataHub on AWS
On AWS, DataHub can run on EKS cluster. By using EKS, you can leverage the power and flexibility of Kubernetes to deploy and scale DataHub components, and take advantage of other AWS services and features, such as IAM, VPC, and CloudWatch, to monitor and secure the DataHub cluster.
DataHub also depends on many underlying infrastructure and services to function, including a message broker, a search engine, graph database, and a relational database like MySQL or PostgreSQL. AWS offers a range of managed and serverless services that can meet the needs of DataHub and simplify its deployment and operation.
- DataHub can use Amazon Managed Streaming for Apache Kafka (MSK) as the messaging layer for metadata ingestion and consumption. MSK is a fully managed Apache Kafka service, so you don't need to handles the provisioning, configuration, and maintenance of Kafka cluster.
- DataHub stores metadata in both relational database and a search engine. For the relational database, this blueprint uses Amazon RDS for MySQL, which is also a managed service that simplifies the setup and operation of MySQL databases. RDS for MySQL also provides the high availability, security, and other features DataHub needs to store the metadata.
- For search engine, this blueprint uses Amazon OpenSearch service to provide fast and scalable search capabilities for the metadata.
- This blueprint deployes a Schema Registry service on EKS for DataHub. You may also choose to use Glue Schema Registry (https://docs.aws.amazon.com/glue/latest/dg/schema-registry.html) instead. Support for Glue Schema Registry will be included in future release of this blueprint.
Deploying the Solution
This blueprint deploys an EKS Cluster into a new VPC by default:
- Creates a new sample VPC, 2 Private Subnets and 2 Public Subnets
- Creates Internet gateway for Public Subnets and NAT Gateway for Private Subnets
You may also deploy to an existing VPC by setting value for create_vpc variable to false and specify vpc_id, private_subnet_ids, and vpc_cidr values.
- Creates EKS Cluster Control plane with public endpoint (for demo reasons only) with core managed node group, on-demand node group and Spot node group for Spark workloads.
- Deploys Metrics server, Cluster Autoscaler, Prometheus server and AMP workspace, and AWS LoadBalancer Controller.
It then provisions the storage services for DataHub.
- Creates security group, and an OpenSearch domain with one data node in each of the private subnets / AZs that EKS cluster is deployed on.
- Creates security group, kms key, and configuration for MSK. Creates the MSK cluster with one broker in each of the private subnets.
- Creates an RDS MySQL db instance with multi-AZ enabled.
Finally it deployes the datahub-prerequisites and datahub helm charts to setup the datahub pods / services on the EKS cluster. Ingress is enabled (as configured in datahub_values.yaml) and AWS LoadBalancer Controller will provision an ALB to expose the DataHub frontend UI.
You may customize the blueprint by changing values in variables.tf, to deploy to a different region (default to us-west-2 ), use different cluster name, number of subnets / AZs, or disable addons like fluentbit
If you already have opensearch service in the account, the service-linked role for OpenSearch exists already. You will need to change default value for variable create_iam_service_linked_role_es to false to avoid error in deployment.
Prerequisites
Ensure that you have installed the following tools on your machine.
Also, you need opensearch service-linked role created in the account. To verify and create the role if needed, run:
aws iam create-service-linked-role --aws-service-name opensearchservice.amazonaws.com || true
If the role has already been successfully created, you will see:
An error occurred (InvalidInput) when calling the CreateServiceLinkedRole operation: Service role name AWSServiceRoleForOpenSearch has been taken in this account, please try a different suffix.
Deploy
Clone the repository
git clone https://github.com/awslabs/data-on-eks.git
Navigate into one of the example directories and run install.sh script
cd data-on-eks/analytics/terraform/datahub-on-eks
chmod +x install.sh
./install.sh
install.sh script runs terraform apply -target for each module in order. The module dependencies are configured so they will be applied in the right sequence when you just run terraform apply. However, provisioning addons and MSK, OpenSearch, and RDS instances often take longer than 15 minutes, causing error when provisioning kubernetes and helm resources/modules afterwards due to expired auth token. So if you use terraform apply instead running install.sh, you may need to run it multiple times and terraform will resume the failed resource with a new token each time and complete the deployment eventually.
Verify Deployment
After the deployment completes, we can access the DataHub UI and test importing metadata from sample datasources. This blueprint creates the Ingress object for the datahub FrontEnd UI with internal LoadBalancer (can only be accessed within the VPC). You may find the URL to the datahub frontend from the output frontend_url, or by running kubectl command below:
kubectl get ingress datahub-datahub-frontend -n datahub
# OUTPUT should looks like below
NAME CLASS HOSTS ADDRESS PORTS AGE
datahub-datahub-frontend <none> * k8s-datahub-datahubd-xxxxxxxxxx-xxxxxxxxxx.<region>.elb.amazonaws.com 80 nn
Copy the ADDRESS field from the output, then open browser and enter the URL as http://<address>/. Enter datahub as the user name when prompted. The default password is set through Kubernetes secret, you can reveal it with command:
kubectl get secret datahub-user-secret -n datahub -o jsonpath='{.data.*}' | base64 -d
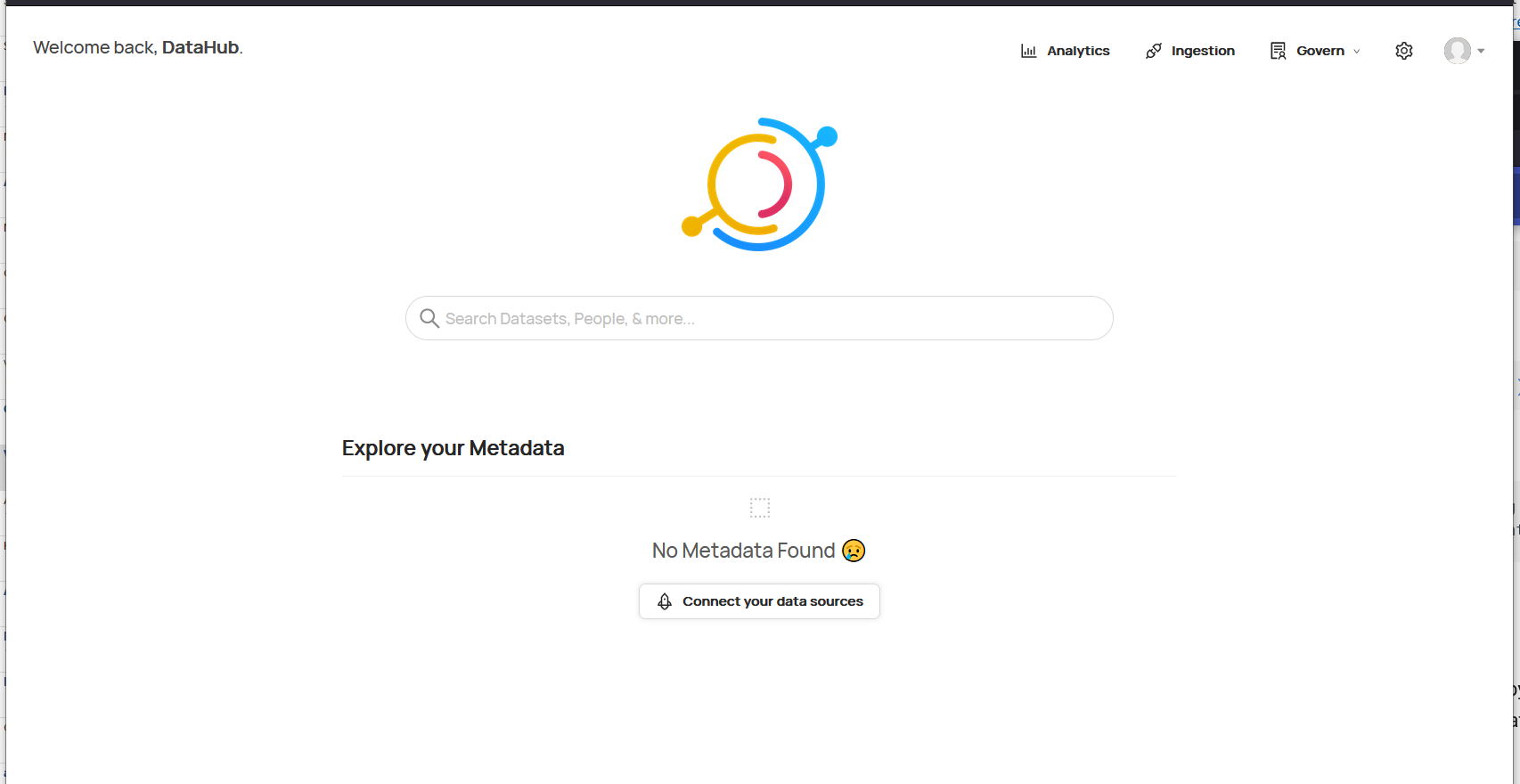
After logging in, we will get the DataHub UI like below.
Testing
Follow steps from this blog to populate metadata from AWS Glue Data Catalog and Amazon Redshift, and business glossary and data lineage, into DataHub.
Cleanup
To clean up your environment, run the cleanup.sh script.script
chmod +x cleanup.sh
./cleanup.sh