Superset Infrastructure Deployment
Apache Superset on EKS
This guide describes how to deploy a scalable Apache Superset platform on Amazon EKS. The stack is provisioned with Terraform and includes Karpenter for node auto-scaling and ArgoCD for GitOps-style application management.
Architecture
This stack provisions the following architecture:
- Amazon EKS Cluster: The core Kubernetes environment for running all applications.
- Apache Superset: The business intelligence and data visualization platform.
- Trino: A distributed SQL query engine used by Superset to query data in S3.
- ArgoCD: Manages the deployment of Superset and Trino in a GitOps fashion.
- Karpenter: Automatically provisions new EKS nodes when needed, allowing the cluster to scale efficiently.
- Amazon RDS: Hosts the metadata database for Superset.
- Amazon S3: Stores the data to be queried by Trino.
Prerequisites
Before deploying, ensure you have the following tools installed:
- AWS CLI - Install Guide
- Terraform (>= 1.0) - Install Guide
- kubectl - Install Guide
- Helm (>= 3.0) - Install Guide
- AWS credentials configured - Run
aws configureor use IAM roles
Step 1: Clone Repository & Navigate
git clone https://github.com/awslabs/data-on-eks.git
cd data-on-eks/data-stacks/Superset-on-eks
Step 2: Customize Stack
Edit the terraform/data-stack.tfvars file to customize settings if required. For example, you can open it with vi, nano, or any other text editor.
Step 3: Deploy Infrastructure
Run the deployment script:
./deploy.sh
If deployment fails:
- Rerun the same command:
./deploy.sh - If it still fails, debug using kubectl commands or raise an issue
Expected deployment time: 15-20 minutes
Step 4: Verify Deployment
The deployment script automatically configures kubectl. Verify the cluster is ready:
# Set kubeconfig
export KUBECONFIG=kubeconfig.yaml
:::tip[Kubeconfig Persistence]
The `export` command only sets the `KUBECONFIG` for your current terminal session. If you open a new terminal, you will need to run this command again. To make it permanent, you can add the line to your shell's profile script (e.g., `~/.bashrc`, `~/.zshrc`) by running:
`echo "export KUBECONFIG=$(pwd)/kubeconfig.yaml" >> ~/.bashrc && source ~/.bashrc`
Replace `~/.bashrc` with your shell's specific profile file if you are not using bash.
:::
Use the following commands to verify that the core components of the stack are running correctly.
```bash
# 1. Verify that the EKS nodes are ready
kubectl get nodes
# Expected: At least 2-3 nodes should be in the 'Ready' state.
# 2. Verify that the Karpenter NodePools are configured
kubectl get nodepools
# Expected: You should see the nodepools defined for the cluster.
# 3. Verify that the ArgoCD applications are Synced and Healthy
kubectl get applications -n argocd
# Expected: All applications should have a SYNC STATUS of 'Synced' and HEALTH STATUS of 'Healthy'.
Expected Output Examples
Nodes:
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION
ip-100-64-112-7.us-west-2.compute.internal Ready <none> 6h16m v1.33.5-eks-113cf36
ip-100-64-113-62.us-west-2.compute.internal Ready <none> 6h16m v1.33.5-eks-113cf36
ip-100-64-12-166.us-west-2.compute.internal Ready <none> 6h10m v1.33.5-eks-113cf36
ArgoCD Applications:
NAME SYNC STATUS HEALTH STATUS
Superset Scyned Healthy
argo-events Synced Healthy
argo-workflows Synced Healthy
aws-for-fluentbit Synced Healthy
...
Karpenter NodePools:
NAME TYPE CAPACITY ZONE NODE READY AGE
general-purpose-d2mrg m7g.4xlarge spot us-west-2a ip-100-64-12-166.us-west-2.compute.internal True 6h12m
general-purpose-d5mgm m7g.4xlarge spot us-west-2a ip-100-64-50-67.us-west-2.compute.internal True 6h15m
memory-optimized-graviton-xkn5x r8g.4xlarge on-demand us-west-2a ip-100-64-59-123.us-west-2.compute.internal True 6h14m
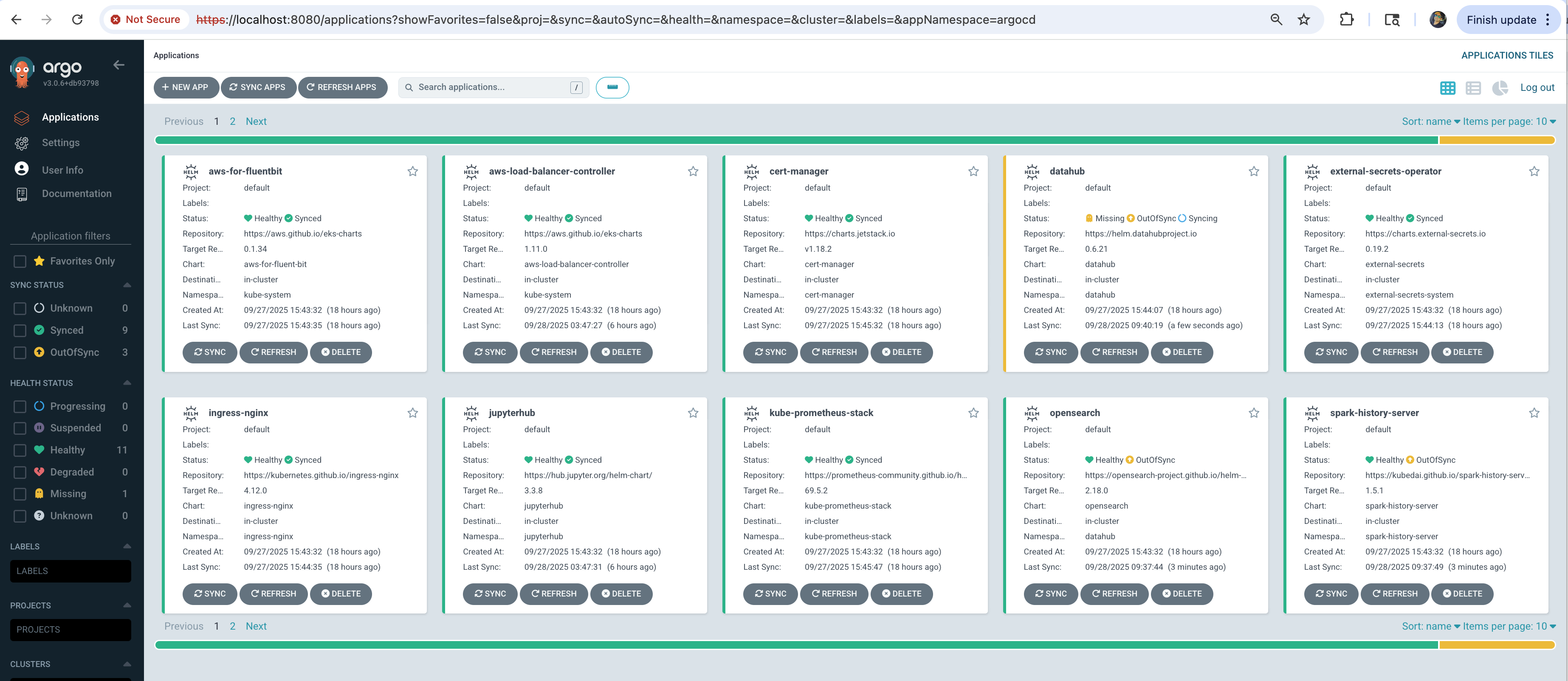
Step 5: Access ArgoCD UI
The deployment script displays ArgoCD credentials at the end. Access the UI:
# Port forward ArgoCD server
kubectl port-forward svc/argocd-server -n argocd 8080:443
Open https://localhost:8080 in your browser:
- Username:
admin - Password: Displayed at end of
deploy.shoutput
It may take additional ~5 minutes for all applications to show Synced and Healthy status.
Troubleshooting
Common Issues
Pods stuck in Pending:
# Check node capacity
kubectl describe nodes
# Check Karpenter logs
kubectl logs -n karpenter -l app.kubernetes.io/name=karpenter
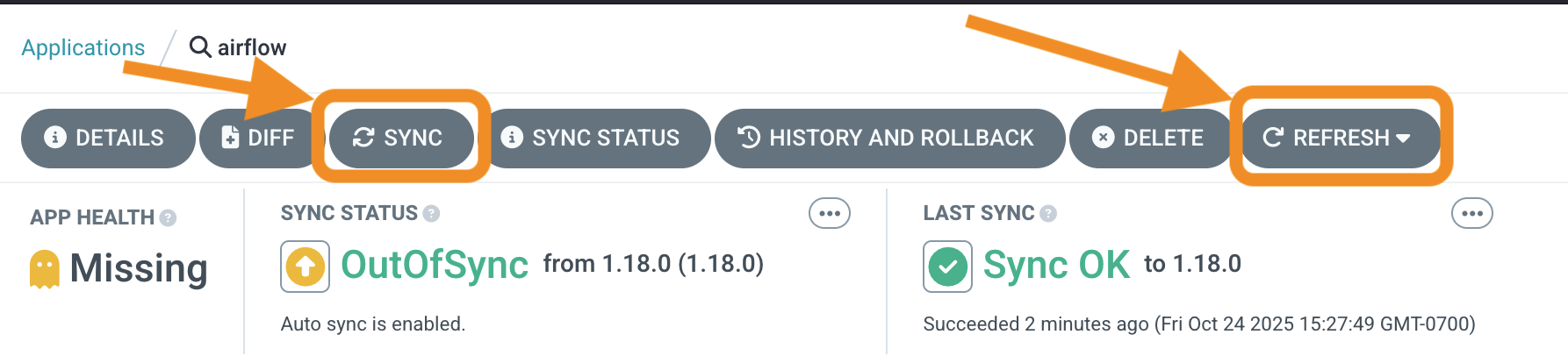
ArgoCD applications not syncing:
# Check ArgoCD application status
kubectl get applications -n argocd
# Check specific application
kubectl describe application Superset-operator -n argocd
Try refreshing and syncing the applications in ArgoCD
Next Steps
With infrastructure deployed, you can now run any Superset examples:
Cleanup
To remove all resources, use the dedicated cleanup script:
# Navigate to stack directory
cd data-on-eks/data-stacks/Superset-on-eks
# Run cleanup script
./cleanup.sh
This command will delete all resources and data. Make sure to backup any important data first.
If cleanup fails:
- Rerun the same command:
./cleanup.sh - Keep rerunning until all resources are deleted
- Some AWS resources may have dependencies that require multiple cleanup attempts