Spark on EKS Infrastructure
Deploy a production-ready Apache Spark platform on Amazon EKS with GitOps, auto-scaling, and observability.
Architecture
This stack deploys Spark Operator on EKS with Karpenter for elastic node provisioning and ArgoCD for GitOps-based application management.
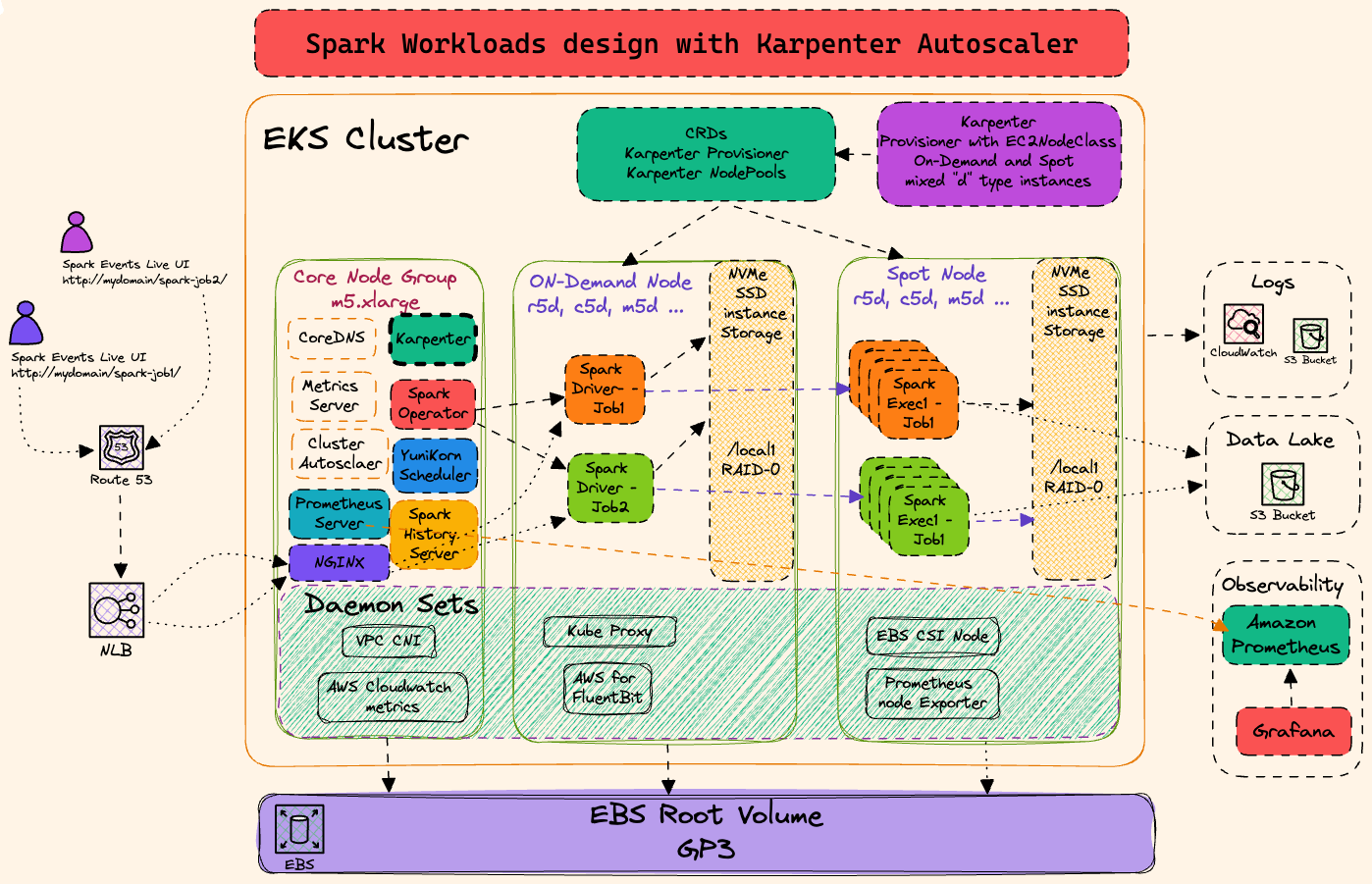
Prerequisites
Before deploying, ensure you have the following tools installed:
- AWS CLI - Install Guide
- Terraform (>= 1.0) - Install Guide
- kubectl - Install Guide
- Helm (>= 3.0) - Install Guide
- AWS credentials configured - Run
aws configureor use IAM roles
Step 1: Clone Repository & Navigate
git clone https://github.com/awslabs/data-on-eks.git
cd data-on-eks/data-stacks/spark-on-eks
Step 2: Customize Stack
Edit the stack configuration file to customize addons and settings:
# Edit configuration file
vi terraform/data-stack.tfvars
What Gets Deployed
This stack deploys a complete data platform with 30+ components automatically via GitOps (ArgoCD).
EKS Managed Addons
Deployed and managed by AWS EKS:
| Component | Purpose | Managed By |
|---|---|---|
coredns | DNS resolution | EKS |
kube-proxy | Network proxy | EKS |
vpc-cni | Pod networking with prefix delegation | EKS |
eks-pod-identity-agent | IAM roles for service accounts | EKS |
aws-ebs-csi-driver | Persistent block storage | EKS |
aws-mountpoint-s3-csi-driver | S3 as volumes | EKS |
metrics-server | Resource metrics API | EKS |
eks-node-monitoring-agent | Node-level monitoring | EKS |
Core Platform Addons
Infrastructure components deployed via ArgoCD:
| Component | Purpose | Category |
|---|---|---|
| Karpenter | Node autoscaling and bin-packing | Compute |
| ArgoCD | GitOps application deployment | Platform |
| cert-manager | TLS certificate automation | Security |
| external-secrets | AWS Secrets Manager integration | Security |
| ingress-nginx | Ingress controller | Networking |
| aws-load-balancer-controller | ALB/NLB integration | Networking |
| kube-prometheus-stack | Prometheus + Grafana monitoring | Observability |
| aws-for-fluentbit | Log aggregation to CloudWatch | Observability |
Data Platform Addons
Data processing and analytics tools:
| Component | Purpose | Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| spark-operator | Apache Spark on Kubernetes | Batch Processing |
| spark-history-server | Spark job history and metrics | Observability |
| yunikorn | Gang scheduling for batch jobs | Scheduling |
| jupyterhub | Interactive notebooks (Python/Scala) | Data Science |
| flink-operator | Stream processing framework | Real-time Analytics |
| strimzi-kafka | Event streaming platform | Event Streaming |
| trino | Distributed SQL query engine | Data Lakehouse |
| argo-workflows | Workflow orchestration (DAGs) | Orchestration |
| argo-events | Event-driven workflow triggers | Event Processing |
| keda | Event-driven pod autoscaling | Autoscaling |
Optional Addons
Configure in terraform/data-stack.tfvars:
name = "spark-on-eks"
region = "us-west-2"
# Optional - disable if not needed
enable_ingress_nginx = true # Ingress controller (default: true)
enable_jupyterhub = true # Notebooks (default: true)
# Optional - enable for specific use cases
enable_celeborn = false # Remote shuffle service
enable_datahub = false # Metadata management
enable_superset = false # Data visualization
enable_raydata = false # Distributed ML/AI
enable_amazon_prometheus = false # Managed Prometheus
To see all available options, check infra/terraform/variables.tf
Step 3: Deploy Infrastructure
Run the deployment script:
./deploy.sh
If deployment fails:
- Rerun the same command:
./deploy.sh - If it still fails, debug using kubectl commands or raise an issue
Expected deployment time: 15-20 minutes
Step 4: Verify Deployment
The deployment script automatically configures kubectl. Verify the cluster is ready:
# Set kubeconfig (done automatically by deploy.sh)
export KUBECONFIG=kubeconfig.yaml
# Verify cluster nodes
kubectl get nodes
# Check all namespaces
kubectl get namespaces
# Verify ArgoCD applications
kubectl get applications -n argocd
Run these commands to verify successful deployment:
# 1. Check nodes are ready
kubectl get nodes
# Expected: 4-5 nodes with STATUS=Ready
# 2. Verify Spark Operator is running
kubectl get pods -n spark-operator
# Expected: spark-operator-controller and webhook pods Running
# 3. Check ArgoCD applications are synced
kubectl get applications -n argocd
# Expected: All apps showing "Synced" and "Healthy"
# 4. Verify Spark CRDs installed
kubectl get crds | grep spark
# Expected: sparkapplications.sparkoperator.k8s.io
# 5. Check Karpenter NodePools ready
kubectl get nodepools
# Expected: 5 pools with READY=True
Expected Output Examples
Nodes:
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION
ip-100-64-106-144.us-west-2.compute.internal Ready <none> 5m44s v1.33.5-eks-113cf36
ip-100-64-37-76.us-west-2.compute.internal Ready <none> 5m43s v1.33.5-eks-113cf36
...
Spark Operator:
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
spark-operator-controller-6bc54d4658-hg2qd 1/1 Running 0 6m20s
spark-operator-webhook-5b5f58597d-hh6b2 1/1 Running 0 6m20s
ArgoCD Applications:
NAME SYNC STATUS HEALTH STATUS
spark-operator Synced Healthy
spark-history-server Synced Healthy
kube-prometheus-stack Synced Healthy
karpenter Synced Healthy
cert-manager Synced Healthy
...
Karpenter NodePools:
NAME NODECLASS NODES READY AGE
general-purpose default 0 True 13m
compute-optimized-x86 default 0 True 13m
compute-optimized-graviton default 0 True 13m
memory-optimized-x86 default 0 True 13m
memory-optimized-graviton default 0 True 13m
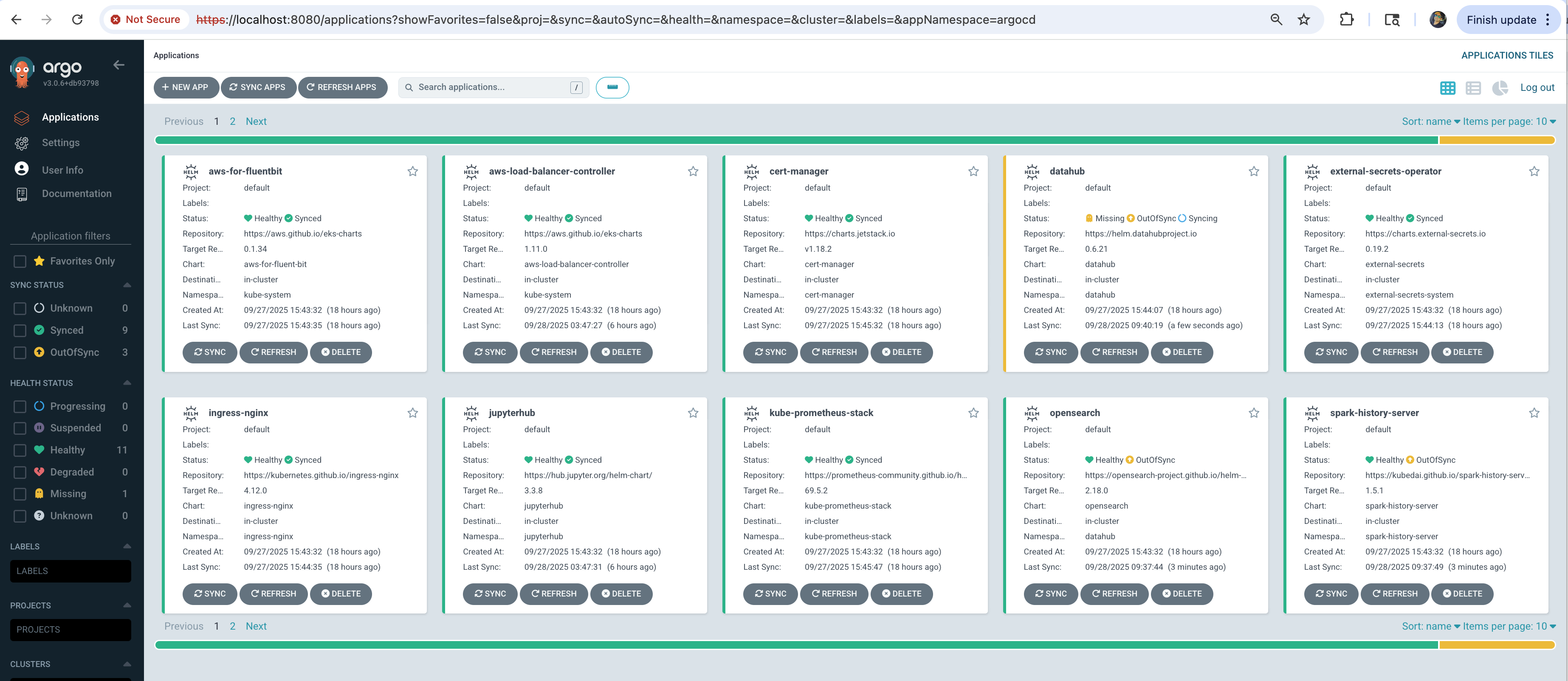
Step 5: Access ArgoCD UI
The deployment script displays ArgoCD credentials at the end. Access the UI:
# Port forward ArgoCD server
kubectl port-forward svc/argocd-server -n argocd 8080:443
Open https://localhost:8080 in your browser:
- Username:
admin - Password: Displayed at end of
deploy.shoutput
All applications should show Synced and Healthy status.
Step 6: Run Test Spark Job
Validate the deployment with a sample PySpark job:
# Get S3 bucket for Spark logs
cd terraform/_local
export S3_BUCKET=$(terraform output -raw s3_bucket_id_spark_history_server)
# Submit test job
cd ../../examples
envsubst < pyspark-pi-job.yaml | kubectl apply -f -
# Watch job status
kubectl get sparkapplications -n spark-team-a -w
What happens:
- Karpenter provisions nodes - Takes ~60s to launch compute-optimized instances
- Driver pod starts - Coordinates the Spark job execution
- Executor pods run - Perform the Pi calculation in parallel
- Job completes - Result:
Pi is roughly 3.141640 - Logs stored in S3 - Accessible via Spark History Server
Expected output:
NAME STATUS ATTEMPTS START FINISH DURATION
pyspark-pi-karpenter COMPLETED 1 2025-10-21T20:08:52Z 2025-10-21T20:11:49Z ~3 min
# Watch job status in real-time
kubectl get sparkapplications -n spark-team-a -w
# View driver logs (shows Pi calculation result)
kubectl logs -n spark-team-a pyspark-pi-karpenter-driver
# Check detailed job status
kubectl describe sparkapplication pyspark-pi-karpenter -n spark-team-a
Troubleshooting
Common Issues
Pods stuck in Pending:
# Check node capacity
kubectl describe nodes
# Check Karpenter logs
kubectl logs -n karpenter -l app.kubernetes.io/name=karpenter
ArgoCD applications not syncing:
# Check ArgoCD application status
kubectl get applications -n argocd
# Check specific application
kubectl describe application spark-operator -n argocd
Next Steps
With infrastructure deployed, you can now run any Spark examples:
Cleanup
To remove all resources, use the dedicated cleanup script:
# Navigate to stack directory
cd data-on-eks/data-stacks/spark-on-eks
# Run cleanup script
./cleanup.sh
If cleanup fails:
- Rerun the same command:
./cleanup.sh - Keep rerunning until all resources are deleted
- Some AWS resources may have dependencies that require multiple cleanup attempts
This command will delete all resources and data. Make sure to backup any important data first.