Observability with Callbacks
Agent Squad provides powerful observability capabilities through a comprehensive callback system that allows you to track, monitor, and analyze the behavior of your multi-agent system. This guide covers the callback system and demonstrates how to integrate with Langfuse for advanced observability.
Callbacks System Overview
The Agent Squad framework implements three main types of callbacks to provide complete visibility into your system:
- Agent Callbacks: Track agent lifecycle, execution, and LLM interactions
- Classifier Callbacks: Monitor request classification and routing decisions
- Tool Callbacks: Observe tool usage and execution
Agent Callbacks
Agent callbacks provide hooks into the agent execution lifecycle:
from agent_squad.agents import AgentCallbacksfrom typing import Optional, Any, UUID
class CustomAgentCallbacks(AgentCallbacks):
async def on_agent_start( self, agent_name: str, input: Any, messages: list[Any], run_id: Optional[UUID] = None, tags: Optional[list[str]] = None, metadata: Optional[dict[str, Any]] = None, **kwargs: Any, ) -> dict: """Called when an agent starts processing""" print(f"Agent {agent_name} starting with input: {input}") return {"start_time": time.time()}
async def on_agent_end( self, agent_name: str, response: Any, messages: list[Any], run_id: Optional[UUID] = None, tags: Optional[list[str]] = None, metadata: Optional[dict[str, Any]] = None, **kwargs: Any, ) -> Any: """Called when an agent completes processing""" print(f"Agent {agent_name} completed")
async def on_llm_start( self, name: str, input: Any, run_id: Optional[UUID] = None, tags: Optional[list[str]] = None, metadata: Optional[dict[str, Any]] = None, **kwargs: Any, ) -> Any: """Called when LLM processing starts""" print(f"LLM {name} starting")
async def on_llm_end( self, name: str, output: Any, run_id: Optional[UUID] = None, tags: Optional[list[str]] = None, metadata: Optional[dict[str, Any]] = None, **kwargs: Any, ) -> Any: """Called when LLM processing ends""" print(f"LLM {name} completed")
async def on_llm_new_token( self, token: str, **kwargs: Any ) -> None: """Called for each new token in streaming responses""" print(f"New token: {token}")// TypeScript callback implementation coming soonClassifier Callbacks
Monitor request classification and routing decisions:
from agent_squad.classifiers import ClassifierCallbacks, ClassifierResultfrom typing import Optional, Any, UUID
class CustomClassifierCallbacks(ClassifierCallbacks):
async def on_classifier_start( self, name: str, input: Any, run_id: Optional[UUID] = None, tags: Optional[list[str]] = None, metadata: Optional[dict[str, Any]] = None, **kwargs: Any, ) -> Any: """Called when classification starts""" print(f"Classifier {name} analyzing: {input}")
async def on_classifier_stop( self, name: str, output: ClassifierResult, run_id: Optional[UUID] = None, tags: Optional[list[str]] = None, metadata: Optional[dict[str, Any]] = None, **kwargs: Any, ) -> Any: """Called when classification completes""" selected_agent = output.selected_agent.name if output.selected_agent else "None" print(f"Classifier selected: {selected_agent} with confidence: {output.confidence}")// TypeScript callback implementation coming soonTool Callbacks
Track tool execution and performance:
from agent_squad.utils import AgentToolCallbacksfrom typing import Optional, Any, UUID
class CustomToolCallbacks(AgentToolCallbacks):
async def on_tool_start( self, tool_name: str, input: Any, run_id: Optional[UUID] = None, tags: Optional[list[str]] = None, metadata: Optional[dict[str, Any]] = None, **kwargs: Any, ) -> Any: """Called when tool execution starts""" print(f"Tool {tool_name} executing with input: {input}")
async def on_tool_end( self, tool_name: str, input: Any, output: dict, run_id: Optional[UUID] = None, **kwargs: Any, ) -> Any: """Called when tool execution completes""" print(f"Tool {tool_name} completed with output: {output}")// TypeScript callback implementation coming soonLangfuse Integration Demo
The Langfuse demo provides a comprehensive example of implementing observability with Langfuse, a powerful open-source observability platform for LLM applications.
Features Demonstrated
The Langfuse demo showcases:
- Complete conversation tracing - Track entire user sessions from start to finish
- Agent classification monitoring - See which agents are selected and why
- LLM usage tracking - Monitor token consumption, costs, and response times
- Tool execution visibility - Observe tool calls and their outcomes
- Performance analytics - Analyze bottlenecks and optimization opportunities
Setup and Configuration
- Install Dependencies:
cd examples/langfuse-demopip install -r requirements.txt- Configure Environment:
# .env fileLANGFUSE_PUBLIC_KEY=your_langfuse_public_keyLANGFUSE_SECRET_KEY=your_langfuse_secret_keyLANGFUSE_HOST=https://cloud.langfuse.com
AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID=your_aws_access_keyAWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY=your_aws_secret_keyAWS_DEFAULT_REGION=your_aws_regionImplementation Example
Here’s how the Langfuse demo implements comprehensive observability:
from langfuse.decorators import observe, langfuse_contextfrom langfuse import Langfusefrom datetime import datetime, timezone
# Initialize Langfuselangfuse = Langfuse()
class LangfuseAgentCallbacks(AgentCallbacks):
async def on_agent_start(self, agent_name, payload_input, messages, **kwargs): """Track agent execution start""" langfuse_context.update_current_observation( input=payload_input, start_time=datetime.now(timezone.utc), name=agent_name, tags=kwargs.get('tags'), metadata=kwargs.get('metadata') )
async def on_agent_end(self, agent_name, response, messages, **kwargs): """Track agent execution completion""" langfuse_context.update_current_observation( end_time=datetime.now(timezone.utc), name=agent_name, output=response, user_id=kwargs.get('user_id'), session_id=kwargs.get('session_id') )
@observe(as_type='generation', capture_input=False) async def on_llm_end(self, name, output, **kwargs): """Track LLM generation with detailed metrics""" input_data = kwargs.get('payload_input', {}) messages = [{'role': 'system', 'content': input_data.get('system')}] messages.extend(input_data.get('messages', []))
langfuse_context.update_current_observation( name=name, input=messages, output=output, model=input_data.get('modelId'), model_parameters=kwargs.get('inferenceConfig'), usage={ 'input': kwargs.get('usage', {}).get('inputTokens'), 'output': kwargs.get('usage', {}).get('outputTokens'), 'total': kwargs.get('usage', {}).get('totalTokens') } )
class LangfuseClassifierCallbacks(ClassifierCallbacks):
async def on_classifier_start(self, name, payload_input, **kwargs): """Track classification start""" inputs = [ {'role': 'system', 'content': kwargs.get('system')}, {'role': 'user', 'content': payload_input} ] langfuse_context.update_current_observation( name=name, start_time=datetime.now(timezone.utc), input=inputs, model=kwargs.get('modelId'), model_parameters=kwargs.get('inferenceConfig') )
async def on_classifier_stop(self, name, output, **kwargs): """Track classification results""" langfuse_context.update_current_observation( output={ 'role': 'assistant', 'content': { 'selected_agent': output.selected_agent.name if output.selected_agent else 'None', 'confidence': output.confidence } }, end_time=datetime.now(timezone.utc), usage={ 'input': kwargs.get('usage', {}).get('inputTokens'), 'output': kwargs.get('usage', {}).get('outputTokens'), 'total': kwargs.get('usage', {}).get('totalTokens') } )
@observe(as_type="generation", name="conversation")def run_conversation(): """Main conversation loop with full tracing""" # Your orchestrator setup and conversation handling pass// TypeScript Langfuse integration coming soonTracing Structure
The Langfuse integration creates a hierarchical trace structure:
Conversation (Generation)├── Classification (Generation)│ └── Classifier LLM Call (Generation)├── Agent Processing (Span)│ ├── Agent LLM Call (Generation)│ └── Tool Calls (Spans)│ ├── Tool Execution (Span)│ └── Tool Results (Span)└── Response Assembly (Span)Trace Visualization
Here’s what a complete trace looks like in the Langfuse dashboard:
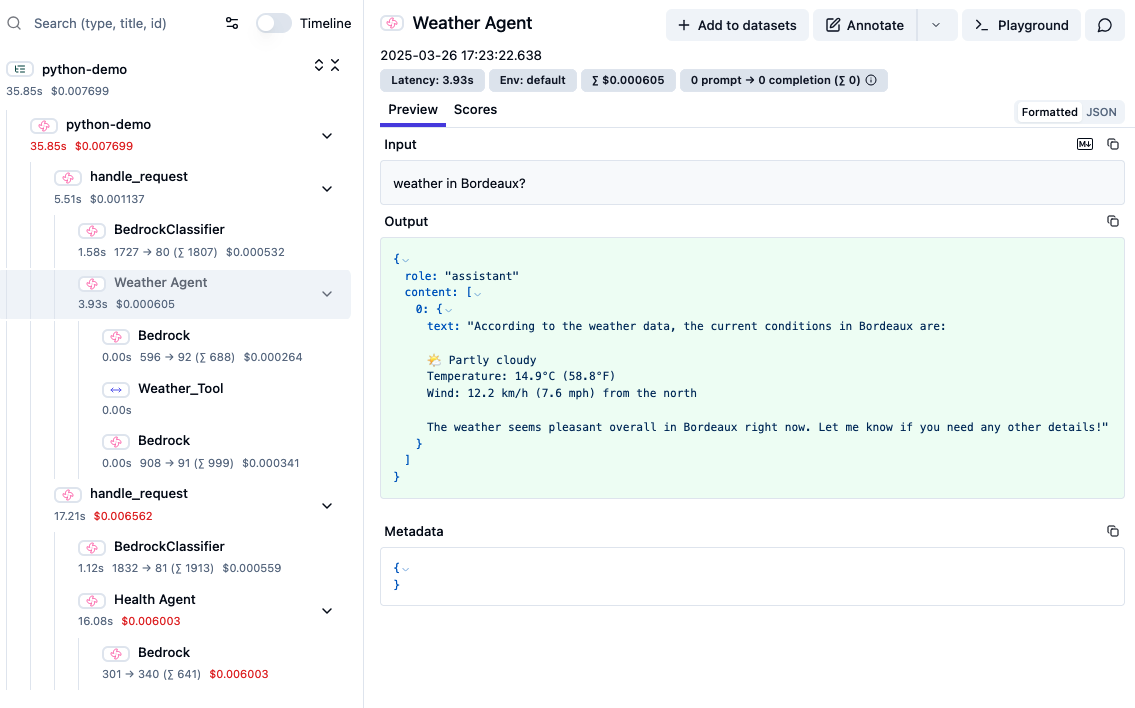
This trace shows the complete flow of a user request, including classification, agent selection, LLM calls, and tool execution, with detailed timing and token usage information.
Analytics and Insights
With Langfuse integration, you can analyze:
- Agent Usage Patterns: Which agents are most frequently selected
- Classification Accuracy: How well the classifier routes requests
- Performance Metrics: Response times, token usage, and costs
- Error Tracking: Failed requests and their causes
- User Behavior: Session patterns and conversation flows
Best Practices
1. Implement Comprehensive Callbacks
class ProductionCallbacks(AgentCallbacks): def __init__(self, logger, metrics_client): self.logger = logger self.metrics = metrics_client
async def on_agent_start(self, agent_name, **kwargs): # Log structured data self.logger.info("agent_start", extra={ "agent_name": agent_name, "user_id": kwargs.get("user_id"), "session_id": kwargs.get("session_id") })
# Send metrics self.metrics.increment("agent.invocations", tags=[f"agent:{agent_name}"])
async def on_llm_end(self, name, output, **kwargs): # Track token usage usage = kwargs.get('usage', {}) self.metrics.gauge("llm.tokens.input", usage.get('inputTokens', 0)) self.metrics.gauge("llm.tokens.output", usage.get('outputTokens', 0))2. Handle Errors Gracefully
class RobustCallbacks(AgentCallbacks): async def on_agent_start(self, **kwargs): try: # Your observability logic pass except Exception as e: # Never let observability break your application logging.error(f"Callback error: {e}")3. Use Sampling for High-Volume Applications
import random
class SampledCallbacks(AgentCallbacks): def __init__(self, sample_rate=0.1): self.sample_rate = sample_rate
async def on_agent_start(self, **kwargs): if random.random() < self.sample_rate: # Only trace a percentage of requests await self.full_trace(**kwargs)4. Correlate Across Services
class CorrelatedCallbacks(AgentCallbacks): async def on_agent_start(self, **kwargs): # Propagate trace context across service boundaries trace_id = kwargs.get('trace_id') or generate_trace_id() self.set_trace_context(trace_id)Integration with Other Observability Tools
The callback system is designed to work with various observability platforms:
OpenTelemetry
from opentelemetry import trace
class OTelCallbacks(AgentCallbacks): def __init__(self): self.tracer = trace.get_tracer(__name__)
async def on_agent_start(self, agent_name, **kwargs): with self.tracer.start_as_current_span(f"agent_{agent_name}") as span: span.set_attribute("agent.name", agent_name) span.set_attribute("user.id", kwargs.get("user_id"))DataDog
from ddtrace import tracer
class DataDogCallbacks(AgentCallbacks): async def on_agent_start(self, agent_name, **kwargs): with tracer.trace("agent.process", service="agent-squad") as span: span.set_tag("agent.name", agent_name) span.set_tag("user.id", kwargs.get("user_id"))Custom Metrics
import timefrom prometheus_client import Counter, Histogram
AGENT_INVOCATIONS = Counter('agent_invocations_total', 'Agent invocations', ['agent_name'])AGENT_DURATION = Histogram('agent_duration_seconds', 'Agent processing time', ['agent_name'])
class MetricsCallbacks(AgentCallbacks): async def on_agent_start(self, agent_name, **kwargs): AGENT_INVOCATIONS.labels(agent_name=agent_name).inc() kwargs['start_time'] = time.time()
async def on_agent_end(self, agent_name, **kwargs): duration = time.time() - kwargs.get('start_time', 0) AGENT_DURATION.labels(agent_name=agent_name).observe(duration)Running the Langfuse Demo
To see the observability system in action:
- Start the demo:
cd examples/langfuse-demopython main.py- Interact with the system:
You: What's the weather in San Francisco?You: Tell me about AI trendsYou: How to improve my sleep?- View traces in Langfuse:
- Navigate to your Langfuse dashboard
- Explore conversation traces
- Analyze agent selection patterns
- Monitor performance metrics
The demo provides a complete template for implementing production-ready observability in your Agent Squad applications.