Introduction
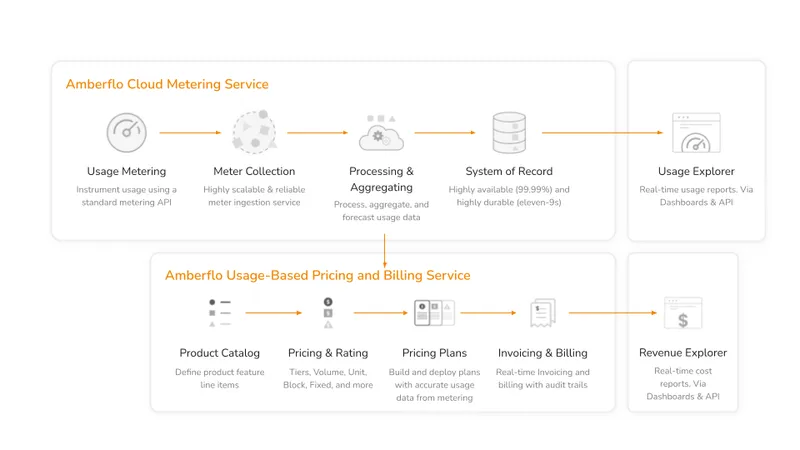
Amberflo is a cloud-based platform designed to help businesses implement and manage metering, usage-based billing, and analytics for their SaaS (Software as a Service) products and services. Amberflo offers a robust platform for real-time tracking, metering and billing of usage events such as LLM tokens, API transactions, and consumption of compute, storage, and network resources, enabling precise billing based on actual usage. Whether you’re managing a subscription-based business model or billing customers per unique user, Amberflo’s billing cloud streamlines the invoicing process and integrates seamlessly with popular payment gateways like Stripe or ERP systems like Netsuite, ensuring smooth, automated customer invoicing and payment collection.
This module enables precise near real-time metering and usage based billing for any Data platforms, SaaS or AI applications. It extends AWS SaaS Builder ToolKit (SBT) capability by integrating Amberflo’s cloud native solution to enable builders to track, meter and bill usage events such as LLM tokens, API transactions, and consumption of compute, storage, and network resources in near real-time. With this integration, you can effortlessly implement a modern, usage-based billing for your SaaS and GenAI applications out-of-the-box.
Installation instructions
Prerequisites
-
Deploy a SBT Project: If you don't already have a SBT project deployed, follow AWS SBT's tutorial to deploy the sample hello-cdk project with a ControlPlane and CoreApplicationPlane.
-
Amberflo Account: You need an Amberflo account for this project. If you don’t have an Amberflo account, you can sign up for one here: Amberflo Signup.
-
API Key Secret: After signing up, the Amberflo API Key must be stored as a secret in AWS Secrets Manager. The application by default expects the secret to be created with the name AmberfloApiKey. However, you can create a secret with your own custom name and pass it in as a parameter to AmberfloMetering.
Secret Name:The name of the secret in AWS Secrets Manager
Secret Key:The key within the secret JSON that contains the API Key
Obtaining the Plugin
Option 1: Clone the repository
git clone https://github.com/amberflo/sbt-aws-amberflo.git
Option 2: Download the latest release Visit the sbt-aws-amberflo releases and download the latest version.
Installation Steps
Within your SBT project directory, install aws-sbt-amberflo via the following command:
npm install --save sbt-aws-amberflo
Configuration
Add AmberfloMetering to Your Control Plane
Instantiate the AmberfloMetering construct in your AWS CDK stack. Here’s an example TypeScript code snippet:
import { Stack } from 'aws-cdk-lib';
import { Construct } from 'constructs';
import * as sbt from '@cdklabs/sbt-aws';
import { AmberfloMetering } from 'sbt-aws-amberflo';
export class ControlPlaneStack extends Stack {
constructor(scope: Construct, id: string, props: any) {
super(scope, id, props);
const amberfloMetering = new AmberfloMetering(this, 'AmberfloMetering', {
amberfloAPIKeySecretName: 'YourSecretName',
amberfloAPIKeySecretId: 'YourSecretId',
});
const controlPlane = new sbt.ControlPlane(this, 'ControlPlane', {
metering: amberfloMetering,
});
}
}
Provision a Meter
Once you deploy your updated stack, you can create and manage meters using the provided API endpoints. Here’s how you can create a meter:
METER=$(jq --null-input \
'{
"label": "SBT Meter",
"meterApiName": "sbt-meter",
"meterType": "sum_of_all_usage"
}')
echo "creating meter..."
curl --request POST \
--url "${CONTROL_PLANE_API_ENDPOINT}meters" \
--header "Authorization: Bearer ${ACCESS_TOKEN}" \
--header 'content-type: application/json' \
--data "$METER" | jq
The above 3 properties are the required properties for creating a meter. You can also pass in additional properties while creating a meter. See more on creating meters in Amberflo.
Update a Meter
Once you deploy your updated stack, you can update meters using the provided API endpoint. Here’s how you can update a meter:
UPDATE_METER=$(jq --null-input \
'{
"label": "SBT trial meter",
"meterApiName": "sbt-trial",
"meterType": "sum_of_all_usage"
}')
echo "updating meter..."
curl --request PUT \
--url "${CONTROL_PLANE_API_ENDPOINT}meters/<meter-id>" \
--header "Authorization: Bearer ${ACCESS_TOKEN}" \
--header 'content-type: application/json' \
--data "$UPDATE_METER" | jq
Get a Meter
You can get a meter by id using the provided API endpoint. Here’s how you can get a meter:
curl --request GET \
--url "${CONTROL_PLANE_API_ENDPOINT}meters/<meterId>" \
--header "Authorization: Bearer ${ACCESS_TOKEN}" \
--silent | jq
List all Meters
You can list all meters using the provided API endpoint. Here’s how you can list all meter:
curl --request GET \
--url "${CONTROL_PLANE_API_ENDPOINT}meters/<meterId>" \
--header "Authorization: Bearer ${ACCESS_TOKEN}" \
--silent | jq
Delete a Meter
You can delete a meter by id using the provided API endpoint. Here’s how you can delete a meter:
curl --request DELETE \
--url "${CONTROL_PLANE_API_ENDPOINT}meters/<meterId>" \
--header "Authorization: Bearer ${ACCESS_TOKEN}" \
--silent | jq
Ingest Usage Events
To ingest usage events, application or service in the application plane must emit events that represent usage metrics, which will be processed by the ingestUsageEventFunction Lambda function.
Event details must contain the following required properties: ● tenantId: The identifier of the tenant to associate with the usage. ● meterApiName: The name of the meter as used in the createMeter. ● meterValue: The quantity or amount of usage to record for a tenant. These properties are necessary to accurately track and attribute usage metrics. You can also pass in additional values for dimensions, if the meter has dimensions defined.
Example
const putEventsResponse = eventManager.eventBus.putEvents({
entries: [{
detail: {
"tenantId": <tenantId>,
"meterApiName": <meterApiName as used in create meter>,
"meterValue": <usage value that is to be recorded>
},
detailType: DetailType.INGEST_USAGE,
source: eventManager.applicationPlaneEventSource,
}],
});
The ingestUsageEventFunction Lambda function will be triggered to handle this event and send the data to Amberflo for processing.
Note: the eventManager is the eventManager passed to the CoreApplicationPlane
Fetch Usage Data
To fetch usage data, use the API endpoint to retrieve data based on your meter API name: Example
METER_API_NAME = 'sbt-meter'
START_TIME = 1724630400
END_TIME = 1724716800
curl --request GET \
--url "${CONTROL_PLANE_API_ENDPOINT}usage/<meterId>?meterApiName=${METER_API_NAME}&startTimeInSeconds=${START_TIME}&endTimeInSeconds=${END_TIME}" \
--header "Authorization: Bearer ${ACCESS_TOKEN}" \
--silent | jq
The meterApiName id not provided in the query string will be fetched using the meterId path parameter. The startTimeInSeconds and endTimeInSeconds are optional and default to (current time - 24hrs) and current time.
Canceling incorrect usage events
There are occasions where a meter event source may send or report incorrect or erroneous meters. Amberflo provides the ability to cancel (undo) one or more meter events as needed. See detailed guide on canceling usage events. Example
FILTER=$(jq --null-input \
'{
"id": "sbt-filtering-rule",
"meterApiName": "sbt-trial",
"ingestionTimeRange": {
"startTimeInSeconds": 1724367600,
"endTimeInSeconds": 1724371200
}
}')
echo "creating filtering rule for canceling usage events..."
curl --request DELETE \
--url "${CONTROL_PLANE_API_ENDPOINT}usage" \
--header "Authorization: Bearer ${ACCESS_TOKEN}" \
--header 'content-type: application/json' \
--data "$FILTER" | jq
The id, meterApiName and ingestionTimeRange are required parameters. The above command creates a filtering rule that cancels the events for the meter sbt-trial in the given time range. You can also cancel more specific events for specific tenants or based on specific dimensions etc. See the Amberflo API for more details.
Usage Examples
The Amberflo metering implementation provided in this repository allows ISVs to integrate Amberflo with their SBT-based applications. This enables ISVs to:
- Track and analyze usage metrics for their tenants
- Create a more accurate and efficient billing process
The AmberfloMetering construct deploys an AWS Lambda function to handle usage metering. It also provides a set of APIs for creating and updating meters, fetching usage, as well as ingesting usage events and canceling usage events. SaaS admins can use these endpoints for managing the application metering. The following endpoints are created in the control plane
Create Meter: POST /meters
Update Meter: PUT /meters/{meterId}
Ingest Usage: POST /ingest
Cancel Usage: DELETE /usage
Fetch Usage: GET /usage/meterId
Here's a brief overview of how this works:
- Meter Creation: SaaS admins can create meters through the create meter API in control plane or through the Amberflo UI.
- Event Emission: Your application or service emits an ingest usage event with the necessary details to measure usage for a specific meter.
- Lambda Invocation: The ingestUsageEventFunction of AmberfloMetering is invoked automatically upon receiving the event.
- Data Processing: The Lambda function processes the event data and sends it to Amberflo for recording and subsequent usage analysis.
- Fetch Usage: SaaS admins can fetch usage through the fetch usage API in control plane or through the Amberflo UI.
Contributing
We welcome contributions to improve the plugin! Please follow these steps:
- Fork the Repository: Click the "Fork" button on the repository page to create your own copy.
- Create a Branch: Create a new branch for your feature or bug fix git checkout -b my-feature-branch
- Make Changes: Implement your feature or bug fix while adhering to existing coding standards.
- Write Tests: Add tests if applicable.
- Commit Your Changes: git commit -m "Add feature X or fix issue Y"
- Push to Your Fork: git push origin my-feature-branch
- Submit a Pull Request: Open a pull request in the original repository with a clear description of your changes.