Envoy gateway
Organizations deploying AI applications face a fundamental challenge: no single model serves all needs. Developers may choose Claude for long-context analysis, OpenAI for reasoning tasks, and DeepSeek for cost-sensitive workloads. The problem is that each model provider uses different APIs. Without centralized control, teams can't easily switch providers, get visibility into utilization, or enforce quotas.
Envoy AI Gateway is an open source project that solves this challenge by providing a single, scalable OpenAI-compatible endpoint that routes to multiple supported LLM providers. It gives Platform teams cost controls and observability, while developers never touch provider-specific SDKs.
Key objectives of Envoy AI Gateway
- Provide a unified layer for routing and managing LLM/AI traffic
- Support automative failover mechanisms to ensure service reliability
- Ensure end-to-end security, including upstream authorization for LLM/AI traffic
- Implement a policy framework to support usage limiting use cases
- Foster an open-source community to address GenAI-specific routing and quality of service needs
Envoy Gateway Fundamentals
As Envoy AI Gateway builds on top of the standard Kubernetes Gateway API and Envoy Gateway extensions, it's necessary to familiarize yourself with the underlying Envoy Gateway primitives:
- GatewayClass - Defines which controller manages the Gateway. Envoy AI Gateway uses the same GatewayClass as Envoy Gateway.
- Gateway - The entry point for traffic. A Gateway resource defines listeners (HTTP/HTTPS ports). When you create a Gateway, Envoy Gateway deploys the actual Envoy proxy pods and a corresponding Kubernetes Service (typically a LoadBalancer). This is like a Network Load Balancer (although technically you'd still need to attach an NLB to an Envoy Gateway to accept traffic that's external the Kubernetes cluster.)
- HTTPRoute - The instruction for routing traffic HTTP based on hostnames, paths, or headers. Conceptually, this is similar to ingress rules or listener rules in ALB.
- Backend - A Kubernetes Service or an external endpoint.
- BackendTrafficPolicy - Configures connection behavior like timeouts, retries, and rate limiting of an HTTPRoute.
- ClientTrafficPolicy - Configures how the Envoy proxy server behaves with downstream clients.
- EnvoyExtensionPolicy - A way to extend Envoy's traffic processing capabilities.
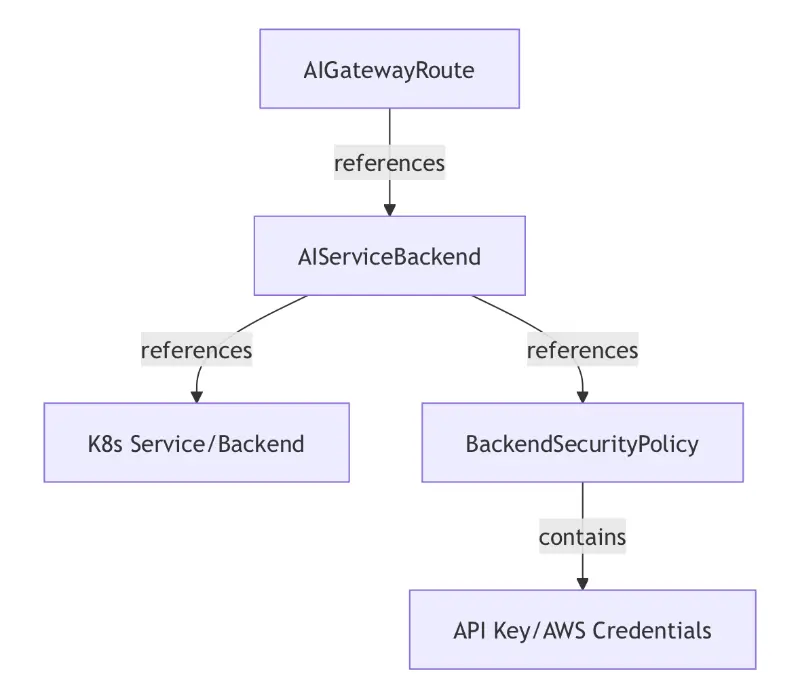
Envoy AI Gateway introduces following CRDs:
- AIGatewayRoute - Defines unified API and routing rules for AI traffic
- AIServiceBackend - Represents individual AI service backends like Bedrock
- BackendSecurityPolicy - Configures authentication for backend access
- BackendTLSPolicy - Defines TLS parameters for backend connections
This envoy gateway blueprint deploys Envoy AI Gateway on Amazon EKS and supports two use cases:
- Multi-model routing
- Rate limiting
Deploying the Solution
👈Deploying self-hosted models
Envoy AI gateway currently supports self-hosted models that can speak OpenAI API schema. We will deploy two models using AI on EKS Inference Charts.
1. Create Hugging Face Token Secret
Create a Kubernetes secret with your Hugging Face token:
kubectl create secret generic hf-token --from-literal=token=your_huggingface_token
2. Deploy Pre-configured Models
Choose from the available pre-configured models and deploy:
These deployments will need GPU/Neuron resources which need to be enabled and cost more than CPU only instances.
# Add helm chart repository
helm repo add ai-on-eks https://awslabs.github.io/ai-on-eks-charts/
helm repo update
# Model 1: Deploy qwen3 model
helm install qwen3-1.7b ai-on-eks/inference-charts -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/awslabs/ai-on-eks-charts/refs/heads/main/charts/inference-charts/values-qwen3-1.7b-vllm.yaml \
--set nameOverride=qwen3 \
--set fullnameOverride=qwen3 \
--set inference.serviceName=qwen3
# Model 2: Deploy gpt oss model
helm install gpt-oss ai-on-eks/inference-charts -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/awslabs/ai-on-eks-charts/refs/heads/main/charts/inference-charts/values-gpt-oss-20b-vllm.yaml \
--set nameOverride=gpt-oss \
--set fullnameOverride=gpt-oss \
--set inference.serviceName=gpt-oss
Verify models up and running
kubectl get pod
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
gpt-oss-67c5bcdd5c-lx9vh 1/1 Running 0 44h
qwen3-b5fdf6bd5-cxkwd 1/1 Running 0 44h
Enabling access to AWS Bedrock models
Access to all Amazon Bedrock foundation models is enabled by default with the correct AWS Marketplace permissions. For more details on managing access to models in Amazon Bedrock, review Access Amazon Bedrock foundation models
Review Supported foundation models in Amazon Bedrock for a list of foundation models available via Amazon Bedrock and relevant model information including Model ID.
Multi-model routing
Route requests to different AI models based on the x-ai-eg-model header. This header enables Envoy AI gateway to identify appropriate route configured within the gateway and routes client traffic to relevant backend kubernetes service. In this case, it's a service that exposes a self-hosted model or Amazon Bedrock model.
Deploy common gateway infrastructure
cd ../../blueprints/gateways/envoy-ai-gateway
kubectl apply -f gateway.yaml
serviceaccount/ai-gateway-dataplane-aws created
gatewayclass.gateway.networking.k8s.io/envoy-gateway created
envoyproxy.gateway.envoyproxy.io/ai-gateway created
gateway.gateway.networking.k8s.io/ai-gateway created
clienttrafficpolicy.gateway.envoyproxy.io/ai-gateway-buffer-limit created
Configure model backends
kubectl apply -f model-backends.yaml
backend.gateway.envoyproxy.io/gpt-oss-backend created
aiservicebackend.aigateway.envoyproxy.io/gpt-oss created
backend.gateway.envoyproxy.io/qwen3-backend created
aiservicebackend.aigateway.envoyproxy.io/qwen3 created
backend.gateway.envoyproxy.io/bedrock-backend created
aiservicebackend.aigateway.envoyproxy.io/bedrock created
backendsecuritypolicy.aigateway.envoyproxy.io/bedrock-policy created
backendtlspolicy.gateway.networking.k8s.io/bedrock-tls created
Configure model routes
kubectl apply -f multi-model-routing/ai-gateway-route.yaml
aigatewayroute.aigateway.envoyproxy.io/multi-model-route created
Test
python3 multi-model-routing/client.py
Expected Output:
🚀 AI Gateway Multi-Model Routing Test
============================================================
Gateway URL: http://k8s-envoygat-envoydef-xxxxxxxxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx.elb.us-west-2.amazonaws.com
=== Testing Qwen3 1.7B ===
Status Code: 200
✅ SUCCESS: Qwen3 - [response content]
=== Testing Self-hosted GPT ===
Status Code: 200
✅ SUCCESS: GPT - [response content]
=== Testing Bedrock Claude ===
Status Code: 200
✅ SUCCESS: Bedrock Claude - [response content]
🎯 Final Results:
• Qwen3 1.7B: ✅ PASS
• GPT OSS 20B: ✅ PASS
• Bedrock Claude: ✅ PASS
📊 Summary: 3/3 models working
Rate limiting
Token-based rate limiting with automatic tracking for AI workloads.
Features:
- Token-based rate limiting (input, output, and total tokens)
- User-based rate limiting using
x-user-idheader - Redis backend for distributed rate limiting (automatically deployed)
- Configurable limits per user per time window
Configure rate limiting
kubectl apply -f rate-limiting/ai-gateway-route.yaml
kubectl apply -f rate-limiting/ai-gateway-rate-limit.yaml
kubectl apply -f rate-limiting/backend-traffic-policy.yaml
Test rate limiting
python3 rate-limiting/client.py
Configuration Details
Routing Configuration
The AI Gateway routes requests based on the x-ai-eg-model header:
| Header Value | Backend | Endpoint | Model Type |
|---|---|---|---|
Qwen/Qwen3-1.7B | qwen3 | /v1/chat/completions | Self-hosted |
openai/gpt-oss-20b | gpt-oss | /v1/chat/completions | Self-hosted |
anthropic.claude-3-haiku-20240307-v1:0 | bedrock | /anthropic/v1/messages | AWS Bedrock |
Bedrock Integration Details
- Authentication: Pod Identity (automatically configured via installation script)
- Schema: AWSAnthropic for native Bedrock support
- Endpoint:
/anthropic/v1/messages(Anthropic Messages API format) - Region: Configurable in
backend-security-policy.yaml(default: us-west-2)
Resources
Important Notes
- Multi-Model Routing: Requires deployed AI model services and AWS Bedrock access
- Rate Limiting: Requires actual AI models that return real token usage data and Redis for storage
- Bedrock Integration: Requires AWS Bedrock API access, proper IAM setup, and Pod Identity configuration
- Authentication: Pod Identity for Bedrock is automatically configured when deploying via the installation script
These are working configuration examples that demonstrate AI Gateway capabilities with real AI model deployments and AWS Bedrock integration.