Testing Resiliency with HyperPod EKS
This guide demonstrates how to test and validate the resiliency features of SageMaker HyperPod when using EKS as the orchestrator. You'll learn how to monitor node health, manually trigger node replacement/reboot, simulate failures, and test job auto-resume functionality.
1.Manual Replacement or Reboot
To watch the status of your cluster nodes, please run the following command:
watch kubectl get nodes -L sagemaker.amazonaws.com/node-health-status
You can press Ctrl-C anytime to exit the watch or execute the line without the watch prefix to show node list just one time.
What if we want to manually replace or reboot a node?
In order to manually reboot a node, we can run the following command, where hyperpod-i-0220224e40218ce3a is the name of the node you want to reboot:
kubectl label node hyperpod-i-0220224e40218ce3a \
sagemaker.amazonaws.com/node-health-status=UnschedulablePendingReboot \
--overwrite=true
Once executed, you would be able to see the node being labeled as UnschedulablePendingReboot and see status change to NotReady.
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION NODE-HEALTH-STATUS
hyperpod-i-0220224e40218ce3a NotReady <none> 6m v1.29.3-eks-ae9a62a UnschedulablePendingReboot
hyperpod-i-06c561302ab149bb7 Ready <none> 4m28s v1.29.3-eks-ae9a62a Schedulable
Soon after, the node would reboot and become available again.
In order to manually replace a node we can run the following command, where hyperpod-i-0220224e40218ce3a is the name of the node you want to replace:
kubectl label node hyperpod-i-0220224e40218ce3a \
sagemaker.amazonaws.com/node-health-status=UnschedulablePendingReplacement \
--overwrite=true
After a while (< 1min), the node status changes from Ready to NotReady:
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION NODE-HEALTH-STATUS
hyperpod-i-0220224e40218ce3a NotReady <none> 13m v1.29.3-eks-ae9a62a UnschedulablePendingReplacement
hyperpod-i-06c561302ab149bb7 Ready <none> 4m28s v1.29.3-eks-ae9a62a Schedulable
After that, the node disappears from the node list:
kubectl get nodes -L sagemaker.amazonaws.com/node-health-status
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION NODE-HEALTH-STATUS
hyperpod-i-06c561302ab149bb7 Ready <none> 5m16s v1.29.3-eks-ae9a62a Schedulable
When a new node is initialized, it is added to the list.
kubectl get nodes -L sagemaker.amazonaws.com/node-health-status
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION NODE-HEALTH-STATUS
hyperpod-i-06c561302ab149bb7 Ready <none> 7m56s v1.29.3-eks-ae9a62a Schedulable
hyperpod-i-0cb64f158c17be463 Ready <none> 16s v1.29.3-eks-ae9a62a Schedulable
You can monitor the progress of the node replacement also on the HyperPod management console.
2.Emulate Instance Failure
This section depicts an example on how to inject an error in order to test automatic node replacement.
connect to one of the nodes in the cluster using SSM agent
aws ssm start-session --target sagemaker-cluster:<hyperpod-cluster-id>_<node-group-name>-<instance-id> --region <aws-region>
Inject the following commands on the instance to emulate the instance failure to trigger instance replacement:
sudo sh -c "sleep 1 && echo \"$(date '+%b %d %H:%M:%S') $(hostname) kernel: NVRM: Xid (PCI:0000:b9:00): 74, pid=<unknown>, name=<unknown>, NVLink: fatal error detected on link 6(0x10000, 0x0, 0x0, 0x0, 0x0, 0x0, 0x0)\" >> /var/log/messages"
change the date to be current before injecting.
Once this is done, you can notice the node label will change to 'UnschedulablePendingReplacement'
kubectl get nodes --show-labels
Inject the following commands on the instance to emulate the instance failure to trigger instance reboot:
sudo sh -c "sleep 1 && echo \"$(date '+%b %d %H:%M:%S') $(hostname) kernel: NVRM: Xid (PCI:0000:b9:00): 73, pid=<unknown>, name=<unknown>, NVLink: fatal error detected on link 6(0x10000, 0x0, 0x0, 0x0, 0x0, 0x0, 0x0)\" >> /var/log/messages"
Once this is done, you will see the node label change to 'UnschedulablePendingReboot'
kubectl get nodes --show-labels
3.Enable Job Auto Resume
This section describes how to run a training job with the SageMaker HyperPod Job auto-resume functionality, which provides a zero-touch resiliency infrastructure to automatically recover a training job from the last saved checkpoint in the event of a hardware failure for clusters. SageMaker HyperPod with EKS currently supports Job auto-resume feature when using Pytorch Training Operator for orchestrating jobs.
Below steps explain how to setup and test Job Auto Resume for your training job.
Add Auto Resume annotations
The following code snippet is an example of how to modify a Kubeflow PyTorch job YAML configuration to enable the job auto-resume functionality. You need to add two annotations and set restartPolicy to OnFailure as shown below. It is recommended to also set nodeSelector to use node that have node-health-status as Schedulable.
#Add auto resume annotations
apiVersion: "kubeflow.org/v1"
kind: PyTorchJob
metadata:
name: fsdp
namespace: kubeflow
annotations: {
sagemaker.amazonaws.com/enable-job-auto-resume: "true",
sagemaker.amazonaws.com/job-max-retry-count: "2"
}
# Set restart policy to onFailure
spec:
....
pytorchReplicaSpecs:
Worker:
replicas: 2
restartPolicy: OnFailure
# Set node selector to only use Schedulable nodes
spec:
....
nodeSelector:
sagemaker.amazonaws.com/node-health-status : Schedulable
--rdzv-conf=timeout=1800 as a parameter to torchrun as shown below. This is needed to account for the time taken to replace the node and run health checks.- /usr/local/bin/torchrun
- --nproc_per_node=8
- --nnodes=2
- --rdzv-conf=timeout=1800
Trigger job failure
Once the above changes are made and the job is running successfully. In order to test auto-resume we can emulate failure by either injecting an error into one of the node or manually triggering node replacement. Please follow the previous sections Emulate Failure / Manual Replacement to trigger job failure.
Check job status and Node status
Once you inject the failure , the job status should automatically show that the job is restarting. Use the kubectl describe command to
kubectl describe pytorchjob <jobname>
Note - Replace the jobname in the above command with the actual jobname.
The Job AutoResume watcher automatically brings down the job and restarts it. You should see in the events section an event for job restar as shown below.
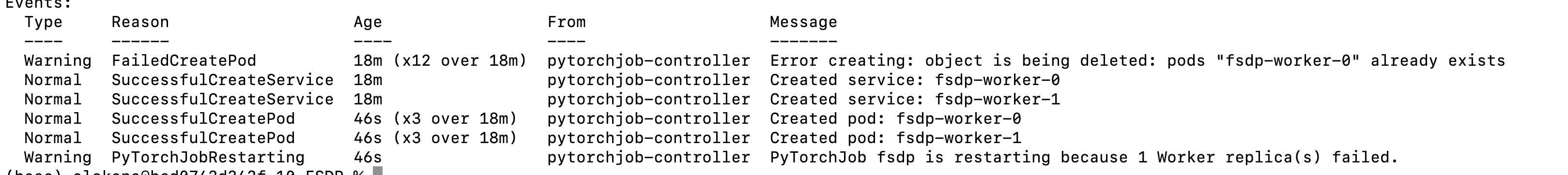
The pod status should show as pending as shown below when you run
kubectl get pods -o wide

You should also notice the faulty node marked as unschedulablependingreplacement when you check the node label
kubectl get nodes -L node.kubernetes.io/instance-type,sagemaker.amazonaws.com/node-health-status,sagemaker.amazonaws.com/deep-health-check-status
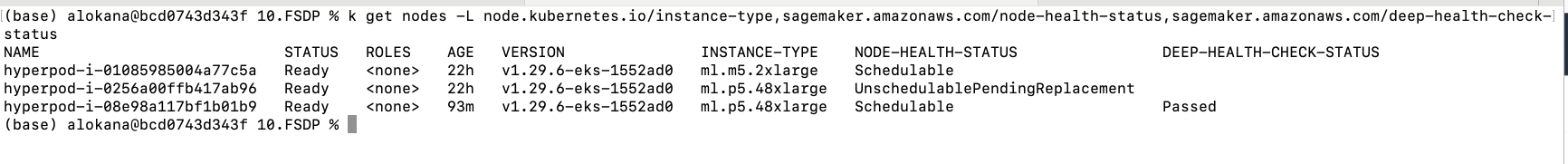
Once a node becomes available the pod that is in pending should get scheduled and the job should restart again.