Manual Deployment Guide
This guide describes how to deploy Kubeflow on Amazon EKS using Cognito as your identity provider. Kubeflow uses Istio to manage internal traffic. In this guide, we will:
- create an Ingress to manage external traffic to the Kubernetes services
- create an Application Load Balancer (ALB) to provide public DNS
- enable TLS authentication for the Load Balancer
- create a custom domain to host Kubeflow (because the certificates needed for TLS are not supported for ALB’s public DNS names)
Prerequisites
Check to make sure that you have the necessary prerequisites.
Background
Read the background section in the Load Balancer guide for information on the requirements for exposing Kubeflow over a Load Balancer.
Read the create domain and certificate section for information on why we use a subdomain for hosting Kubeflow.
(Optional) Automated setup
The rest of the sections in this guide walk you through each step for setting up domain, certificates, and a Cognito userpool using the AWS Console. This guide is intended for a new user to understand the design and details of these setup steps. If you prefer to use automated scripts and avoid human error for setting up the resources for deploying Kubeflow with Cognito, follow the automated setup guide.
1.0 Custom domain and certificates
- Follow the Create a subdomain section of the Load Balancer guide to create a subdomain(e.g.
platform.example.com) for hosting Kubeflow. - Follow the Create certificates for domain section of the Load Balancer guide to create certificates required for TLS.
From this point onwards, we will be creating/updating the DNS records only in the subdomain. All the screenshots of the hosted zone in the following sections/steps of this guide are for the subdomain.
2.0 Cognito User Pool
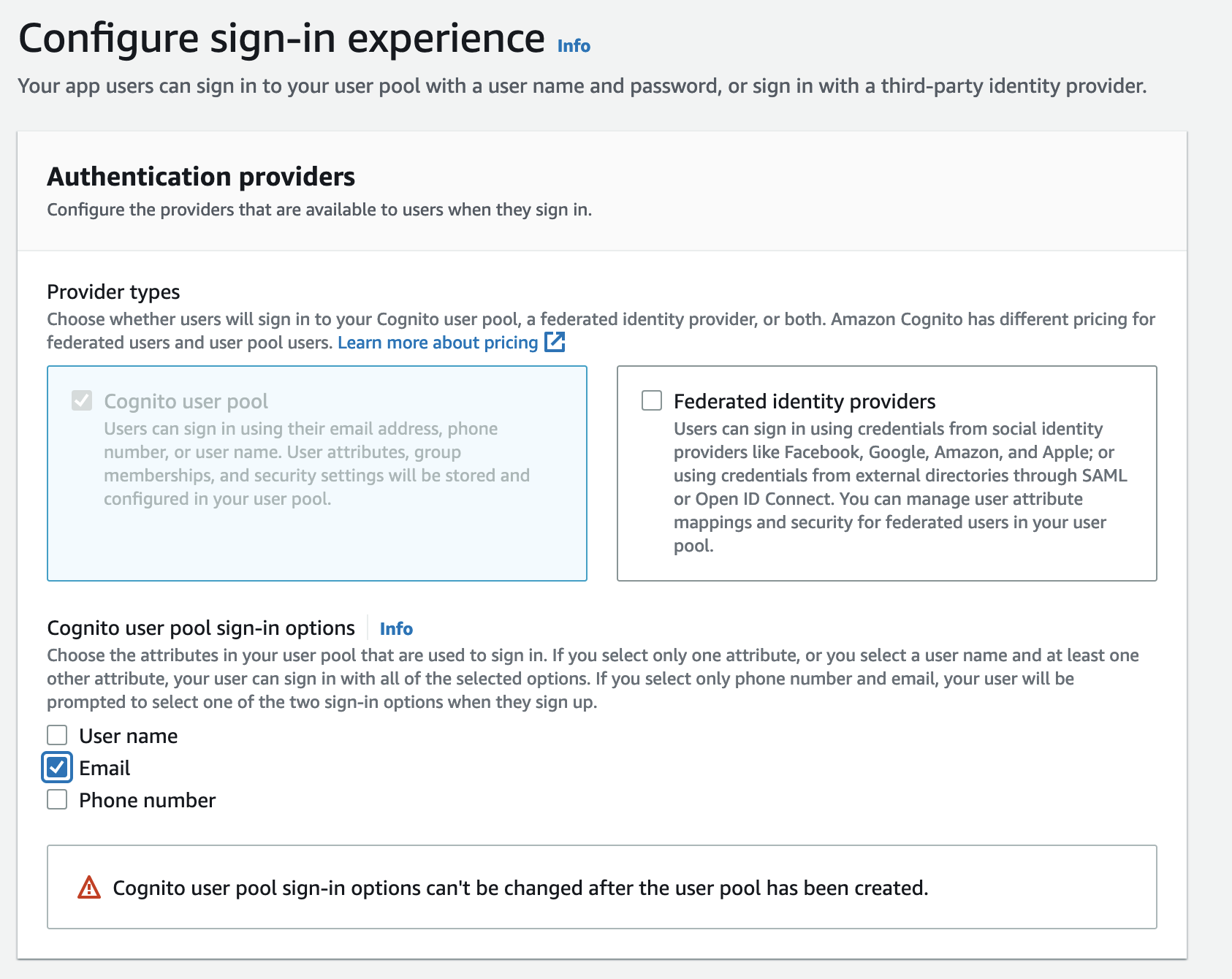
- Create a user pool in Cognito in the same region as your EKS cluster. Type a pool name and choose
Review defaults. - Email is a required user attribute since Kubeflow uses email address as the user identifier for multi-user isolation. See this documentation for example. On the review page, make sure email is selected as a required attribute. If it is not by default, Edit the
Required attributesand selectemail. - On the Policies page, select
Only allow administrators to create usersunderDo you want to allow users to sign themselves up?and save changes. This step is optional but is recommended to have strict control over the users. - Click on
Create poolto create the user pool. - Add an
App clientwith any name and the default options. - In the
App client settings, selectAuthorization code grantflow under OAuth-2.0 and check boxemail,openid,aws.cognito.signin.user.adminandprofilescopes. Also check boxEnabled Identity Providers.- Substitute
example.comin this URL -https://kubeflow.platform.example.com/oauth2/idpresponsewith your domain and use it as the Callback URL(s). - Substitute
example.comin this URL -https://kubeflow.platform.example.comwith your domain and use it as the Sign out URL(s). 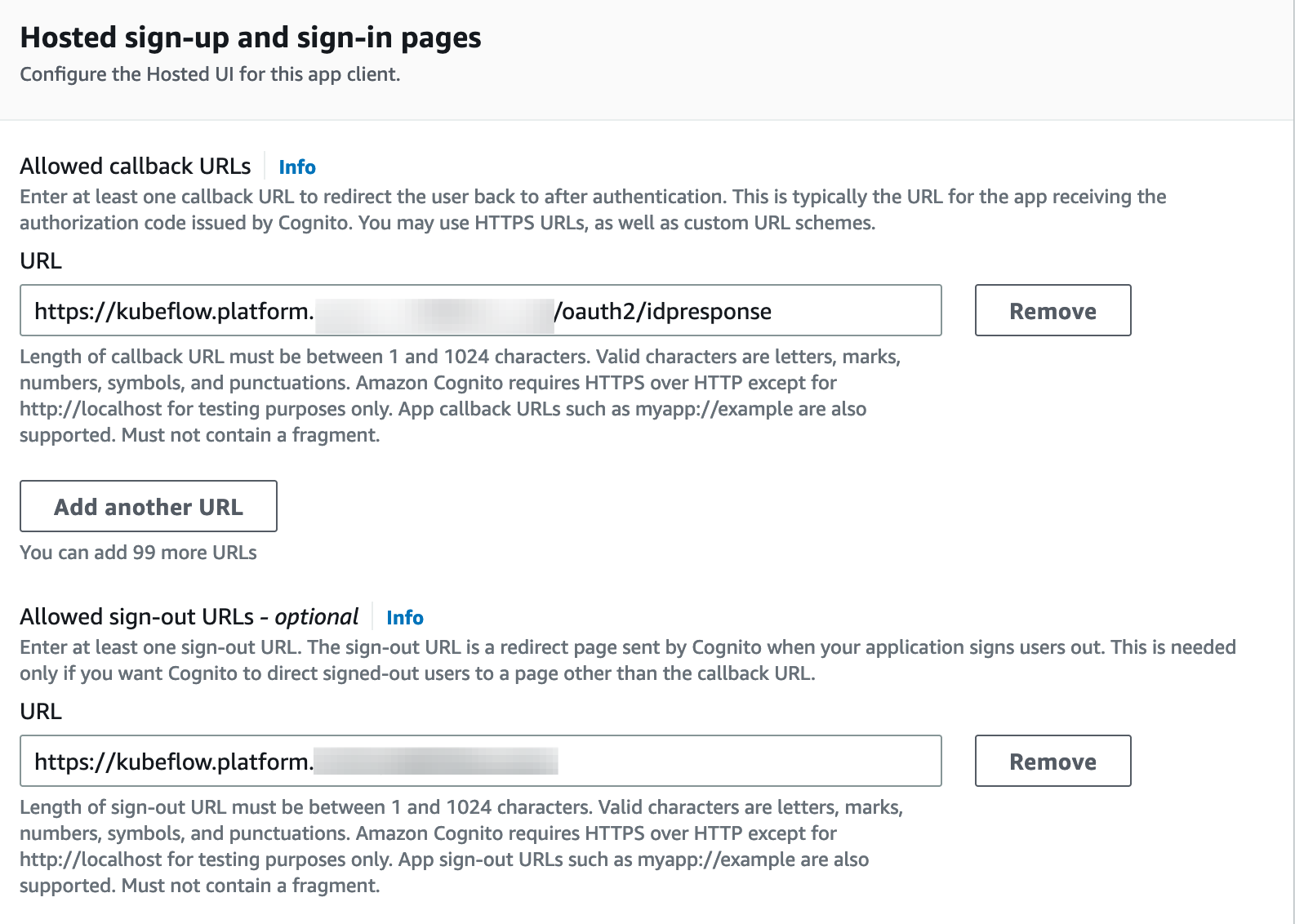
- Substitute
- Add a custom domain to the user pool. In order to add a custom domain to your user pool, you need to specify a domain name, and provide a certificate managed with AWS Certificate Manager (ACM).
- In order to use a custom domain, its root(i.e.
platform.example.com) must have an valid A type record. Create a new record of typeAinplatform.example.comhosted zone with an arbitrary IP for now. Once we have ALB created, we will update this value.- Following is a screenshot of
platform.example.comhosted zone. A record is shown.
- Following is a screenshot of
- If your cluster is not in N.Virginia(us-east-1), create an ACM certificate in us-east-1 for
*.platform.example.comby following the process similar to section 2.0. That is because Cognito requires a certificate in N.Virginia in order to have a custom domain for a user pool. - In the
Domain namechooseUse your domain, typeauth.platform.example.comand select the*.platform.example.comAWS managed certificate you’ve created in N.Virginia. Creating domain takes up to 15 mins.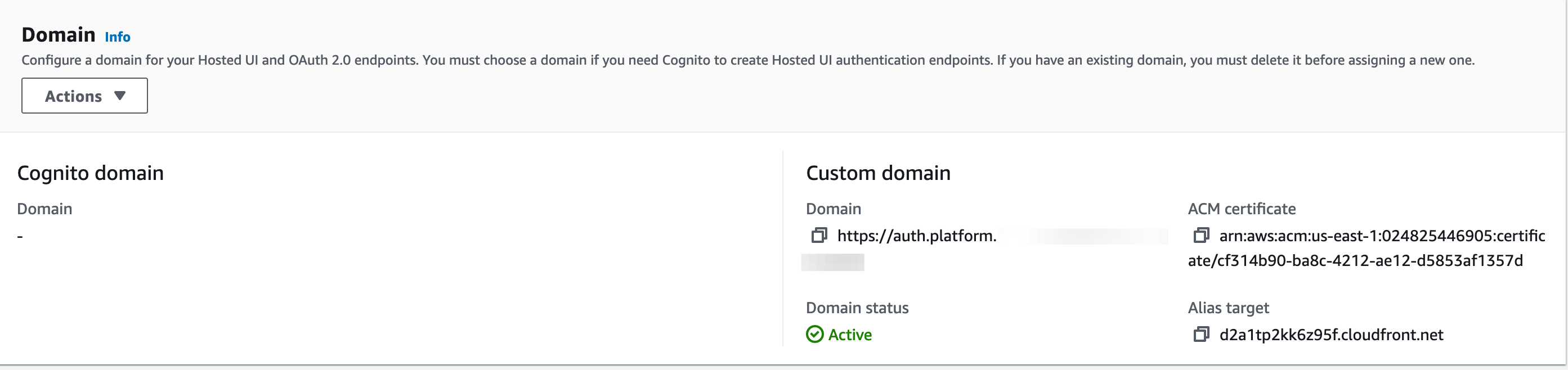
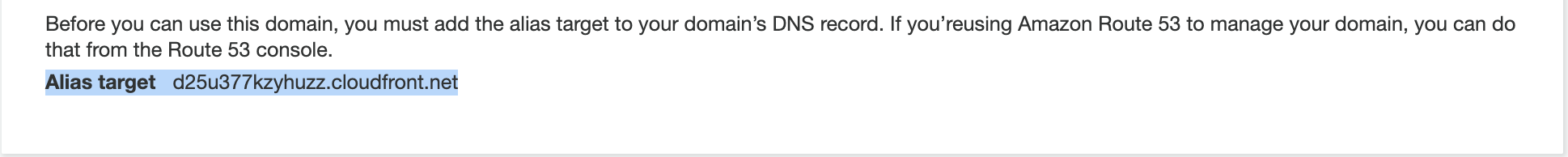
- When it’s created, it will return the
Alias targetCloudFront address.- Screenshot of the CloudFront URL for Cognito Domain name:
- Create a new record of type
Aforauth.platform.example.comwith the value of the CloudFront URL.- Select the
aliastoggle and select Alias to Cloudfront distribution for creating the record 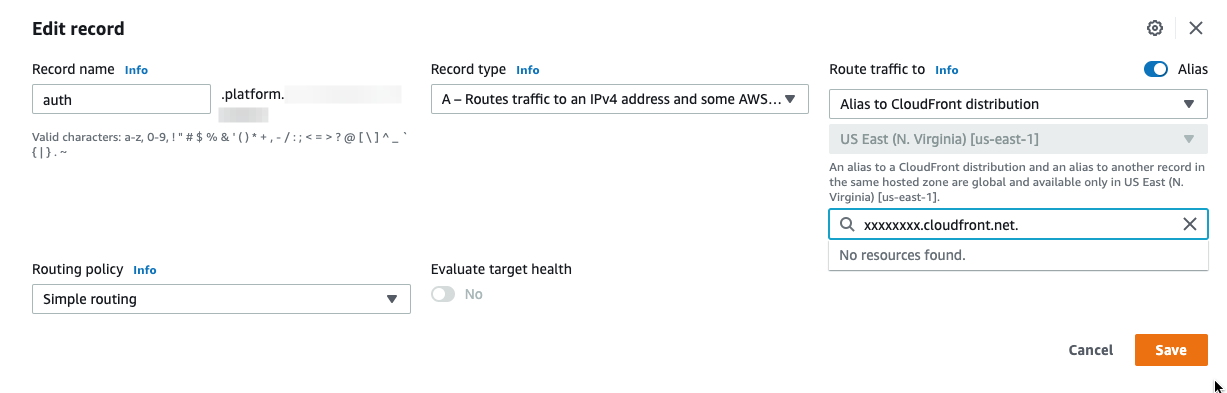
- Following is a screenshot of the A record for
auth.platform.example.cominplatform.example.comhosted zone:
- Select the
- Screenshot of the CloudFront URL for Cognito Domain name:
- In order to use a custom domain, its root(i.e.
3.0 Configure Ingress
- Take note of the following values from the previous step
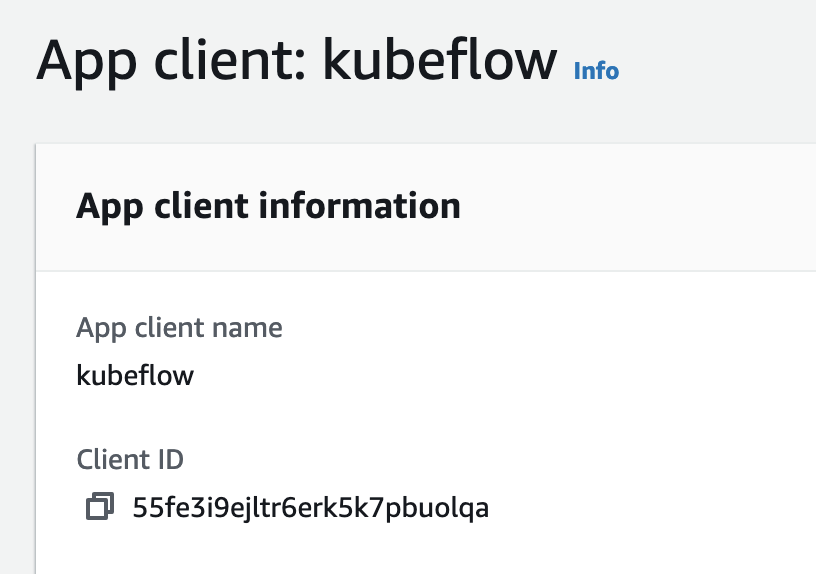
- The Pool ARN of the user pool found in Cognito general settings.
- The App client id, found in Cognito App clients.
- The custom user pool domain (e.g.
auth.platform.example.com), found in the Cognito domain name. - The ARN of the certificate from the Certificate Manager in the region where your platform (for the subdomain) is running.
- signOutURL is the domain that you provided as the Sign out URL(s).
- CognitoLogoutURL is comprised of your CognitoUserPoolDomain, CognitoAppClientId, and your domain that you provided as the Sign out URL(s).
- Export the values:
1.
export CognitoUserPoolArn="<YOUR_USER_POOL_ARN>" export CognitoAppClientId="<YOUR_APP_CLIENT_ID>" export CognitoUserPoolDomain="<YOUR_USER_POOL_DOMAIN>" export certArn="<YOUR_ACM_CERTIFICATE_ARN>" export signOutURL="<YOUR_SIGN_OUT_URL>" export CognitoLogoutURL="https://$CognitoUserPoolDomain/logout?client_id=$CognitoAppClientId&logout_uri=$signOutURL"
- Substitute values for setting up Ingress.
-
printf ' CognitoUserPoolArn='$CognitoUserPoolArn' CognitoAppClientId='$CognitoAppClientId' CognitoUserPoolDomain='$CognitoUserPoolDomain' certArn='$certArn' ' > awsconfigs/common/istio-ingress/overlays/cognito/params.env
-
- Substitute values for setting up AWS authservice.
-
printf ' LOGOUT_URL='$CognitoLogoutURL' ' > awsconfigs/common/aws-authservice/base/params.env
-
- Follow the Configure Load Balancer Controller section of the load balancer guide to setup the resources required the load balancer controller.
4.0 Building manifests and deploying Kubeflow
- Choose one of the two options to deploy kubeflow:
- [Option 1] Install with a single command:
while ! kustomize build deployments/cognito | kubectl apply -f -; do echo "Retrying to apply resources"; sleep 30; done - [Option 2] Install individual components:
# Kubeflow namespace kustomize build upstream/common/kubeflow-namespace/base | kubectl apply -f - # Kubeflow Roles kustomize build upstream/common/kubeflow-roles/base | kubectl apply -f - # Istio kustomize build upstream/common/istio-1-11/istio-crds/base | kubectl apply -f - kustomize build upstream/common/istio-1-11/istio-namespace/base | kubectl apply -f - kustomize build upstream/common/istio-1-11/istio-install/base | kubectl apply -f - # Cert-Manager kustomize build upstream/common/cert-manager/cert-manager/base | kubectl apply -f - kustomize build upstream/common/cert-manager/kubeflow-issuer/base | kubectl apply -f - # KNative kustomize build upstream/common/knative/knative-serving/overlays/gateways | kubectl apply -f - kustomize build upstream/common/knative/knative-eventing/base | kubectl apply -f - kustomize build upstream/common/istio-1-11/cluster-local-gateway/base | kubectl apply -f - # Kubeflow Istio Resources kustomize build upstream/common/istio-1-11/kubeflow-istio-resources/base | kubectl apply -f - # Kubeflow Pipelines # reapply manifest if you see an error kustomize build upstream/apps/pipeline/upstream/env/cert-manager/platform-agnostic-multi-user | kubectl apply -f - # KServe kustomize build awsconfigs/apps/kserve | kubectl apply -f - kustomize build upstream/contrib/kserve/models-web-app/overlays/kubeflow | kubectl apply -f - # KFServing - This is an optional component and required only if you are not ready to migrate to KServe. We recommend migrating to KServe as soon as possible kustomize build upstream/apps/kfserving/upstream/overlays/kubeflow | kubectl apply -f - # Katib kustomize build upstream/apps/katib/upstream/installs/katib-with-kubeflow | kubectl apply -f - # Central Dashboard kustomize build upstream/apps/centraldashboard/upstream/overlays/kserve | kubectl apply -f - # Notebooks kustomize build upstream/apps/jupyter/notebook-controller/upstream/overlays/kubeflow | kubectl apply -f - kustomize build awsconfigs/apps/jupyter-web-app | kubectl apply -f - # Admission Webhook kustomize build upstream/apps/admission-webhook/upstream/overlays/cert-manager | kubectl apply -f - # Profiles + KFAM kustomize build upstream/apps/profiles/upstream/overlays/kubeflow | kubectl apply -f - # Volumes Web App kustomize build upstream/apps/volumes-web-app/upstream/overlays/istio | kubectl apply -f - # Tensorboard kustomize build upstream/apps/tensorboard/tensorboards-web-app/upstream/overlays/istio | kubectl apply -f - kustomize build upstream/apps/tensorboard/tensorboard-controller/upstream/overlays/kubeflow | kubectl apply -f - # Training Operator kustomize build upstream/apps/training-operator/upstream/overlays/kubeflow | kubectl apply -f - # AWS Telemetry - This is an optional component. See usage tracking documentation for more information kustomize build awsconfigs/common/aws-telemetry | kubectl apply -f - # Ingress kustomize build awsconfigs/common/istio-ingress/overlays/cognito | kubectl apply -f - # ALB controller kustomize build awsconfigs/common/aws-alb-ingress-controller/base | kubectl apply -f - # AWS Authservice kustomize build awsconfigs/common/aws-authservice/base | kubectl apply -f -
- [Option 1] Install with a single command:
5.0 Updating the domain with ALB address
- Check if ALB is provisioned. This may take a few minutes.
-
kubectl get ingress -n istio-system Warning: extensions/v1beta1 Ingress is deprecated in v1.14+, unavailable in v1.22+; use networking.k8s.io/v1 Ingress NAME CLASS HOSTS ADDRESS PORTS AGE istio-ingress <none> * k8s-istiosys-istioing-xxxxxx-110050202.us-west-2.elb.amazonaws.com 80 15d - If
ADDRESSis empty after a few minutes, see ALB fails to provision in the troubleshooting guide.
-
- When ALB is ready, copy the DNS name of that load balancer and create a CNAME entry to it in Route53 under subdomain (
platform.example.com) for*.platform.example.com - Update the type
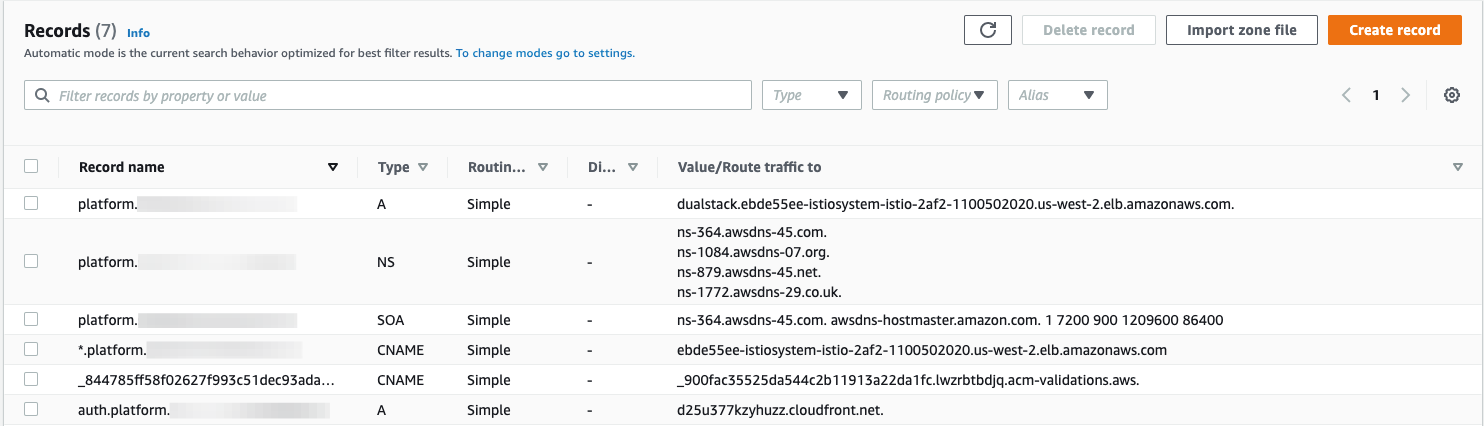
Arecord created in section forplatform.example.comusing ALB DNS name. Change from127.0.0.1→ ALB DNS name. You have to use alias form underAlias to application and classical load balancerand select region and your ALB address. - Screenshot of all the record sets in hosted zone for reference
6.0 Connecting to central dashboard
- The central dashboard should now be available at
https://kubeflow.platform.example.com. Before connecting to the dashboard:- Head over to the Cognito console and create some users in
Users and groups. These are the users who will log in to the central dashboard. - Create a Profile for a user by following the steps in the Manual Profile Creation. The following is an example Profile for reference:
-
apiVersion: kubeflow.org/v1beta1 kind: Profile metadata: # replace with the name of profile you want, this will be user's namespace name name: namespace-for-my-user namespace: kubeflow spec: owner: kind: User # replace with the email of the user name: my_user_email@kubeflow.com
-
- Head over to the Cognito console and create some users in
- Open the central dashboard at
https://kubeflow.platform.example.com. It will redirect to Cognito for login. Use the credentials of the user that you just created a Profile for in previous step.
Note: It might a few minutes for DNS changes to propagate and for your URL to work. Check if the DNS entry propogated with the Google Admin Toolbox
7.0 Uninstall Kubeflow
To delete the resources created in this guide, refer to the Uninstall section in Automated Cognito deployment guide