Implementare l'API del Gioco e il server MCP dell'Inventario
Task 1: Implementare la Game API
Sezione intitolata “Task 1: Implementare la Game API”Implementeremo le seguenti API in questa sezione:
saveGame- crea o aggiorna un gioco.queryGames- restituisce una lista paginata di giochi salvati precedentemente.saveAction- salva un’azione per un determinato gioco.queryActions- restituisce una lista paginata di tutte le azioni relative a un gioco.queryInventory- restituisce una lista paginata degli oggetti nell’inventario di un giocatore.
Schema dell’API
Sezione intitolata “Schema dell’API”Per definire gli input e gli output della nostra API, creiamo il nostro schema utilizzando Zod nel file packages/game-api/src/schema/index.ts come segue:
import { z } from 'zod';
export const QueryInputSchema = z.object({ cursor: z.string().optional(), limit: z.number().optional().default(100),});export type IQueryInput = z.TypeOf<typeof QueryInputSchema>;
export const ActionSchema = z.object({ playerName: z.string(), timestamp: z.iso.datetime(), role: z.enum(['assistant', 'user']), content: z.string(),});export type IAction = z.TypeOf<typeof ActionSchema>;
export const GameSchema = z.object({ playerName: z.string(), genre: z.enum(['zombie', 'superhero', 'medieval']), lastUpdated: z.iso.datetime(),});export type IGame = z.TypeOf<typeof GameSchema>;
export const ItemSchema = z.object({ playerName: z.string(), itemName: z.string(), emoji: z.string().optional(), lastUpdated: z.iso.datetime(), quantity: z.number(),});export type IItem = z.TypeOf<typeof ItemSchema>;
export const createPaginatedQueryOutput = <ItemType extends z.ZodTypeAny>( itemSchema: ItemType,) => { return z.object({ items: z.array(itemSchema), cursor: z.string().nullable(), });};export * from './echo.js'import { z } from 'zod';
export const QueryInputSchema = z.object({ cursor: z.string().optional(), limit: z.number().optional().default(100),});export type IQueryInput = z.TypeOf<typeof QueryInputSchema>;
export const ActionSchema = z.object({ playerName: z.string(), timestamp: z.iso.datetime(), role: z.enum(['assistant', 'user']), content: z.string(),});export type IAction = z.TypeOf<typeof ActionSchema>;
export const GameSchema = z.object({ playerName: z.string(), genre: z.enum(['zombie', 'superhero', 'medieval']), lastUpdated: z.iso.datetime(),});export type IGame = z.TypeOf<typeof GameSchema>;
export const ItemSchema = z.object({ playerName: z.string(), itemName: z.string(), emoji: z.string().optional(), lastUpdated: z.iso.datetime(), quantity: z.number(),});export type IItem = z.TypeOf<typeof ItemSchema>;
export const createPaginatedQueryOutput = <ItemType extends z.ZodTypeAny>( itemSchema: ItemType,) => { return z.object({ items: z.array(itemSchema), cursor: z.string().nullable(), });};Elimina il file packages/game-api/src/schema/echo.ts poiché non lo utilizzeremo in questo progetto.
Modellazione delle entità
Sezione intitolata “Modellazione delle entità”Questo è il diagramma ER per la nostra applicazione.
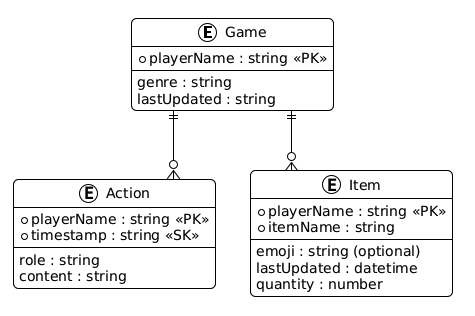
Implementeremo il nostro database in DynamoDB e utilizzeremo la libreria client ElectroDB per semplificare le operazioni. Per installare electrodb e il DynamoDB Client, esegui questo comando:
pnpm add -w electrodb@3.5.3 @aws-sdk/client-dynamodb@3.992.0yarn add electrodb@3.5.3 @aws-sdk/client-dynamodb@3.992.0npm install --legacy-peer-deps electrodb@3.5.3 @aws-sdk/client-dynamodb@3.992.0bun install electrodb@3.5.3 @aws-sdk/client-dynamodb@3.992.0Per definire le entità ElectroDB dal diagramma ER, creiamo il file packages/game-api/src/entities/index.ts:
import { Entity } from 'electrodb';import { DynamoDBClient } from '@aws-sdk/client-dynamodb';
export const createActionEntity = (client: DynamoDBClient = new DynamoDBClient()) => new Entity( { model: { entity: 'Action', version: '1', service: 'game', }, attributes: { playerName: { type: 'string', required: true, readOnly: true }, timestamp: { type: 'string', required: true, readOnly: true, set: () => new Date().toISOString(), default: () => new Date().toISOString(), }, role: { type: 'string', required: true, readOnly: true }, content: { type: 'string', required: true, readOnly: true }, }, indexes: { primary: { pk: { field: 'pk', composite: ['playerName'] }, sk: { field: 'sk', composite: ['timestamp'] }, }, }, }, { client, table: process.env.TABLE_NAME }, );
export const createGameEntity = (client: DynamoDBClient = new DynamoDBClient()) => new Entity( { model: { entity: 'Game', version: '1', service: 'game', }, attributes: { playerName: { type: 'string', required: true, readOnly: true }, genre: { type: 'string', required: true, readOnly: true }, lastUpdated: { type: 'string', required: true, default: () => new Date().toISOString(), }, }, indexes: { primary: { pk: { field: 'pk', composite: ['playerName'] }, sk: { field: 'sk', composite: [], }, }, }, }, { client, table: process.env.TABLE_NAME }, );
export const createInventoryEntity = (client: DynamoDBClient = new DynamoDBClient()) => new Entity( { model: { entity: 'Inventory', version: '1', service: 'game', }, attributes: { playerName: { type: 'string', required: true, readOnly: true }, lastUpdated: { type: 'string', required: true, default: () => new Date().toISOString(), }, itemName: { type: 'string', required: true, }, emoji: { type: 'string', required: false, }, quantity: { type: 'number', required: true, }, }, indexes: { primary: { pk: { field: 'pk', composite: ['playerName'] }, sk: { field: 'sk', composite: ['itemName'] }, }, }, }, { client, table: process.env.TABLE_NAME }, );ElectroDB ci permette non solo di definire i nostri tipi, ma può anche fornire valori predefiniti per certi campi come i timestamp. Inoltre, ElectroDB segue il single-table design, che è la best practice quando si utilizza DynamoDB.
Per preparare il server MCP a interagire con l’inventario, assicuriamoci di esportare l’entità dell’inventario in packages/game-api/src/index.ts:
export type { AppRouter } from './router.js';export { appRouter } from './router.js';export type { Context } from './init.js';export * from './client/index.js';export * from './schema/index.js';export * from './entities/index.js';Definizione delle procedure
Sezione intitolata “Definizione delle procedure”Per implementare i metodi dell’API, apporta le seguenti modifiche in packages/game-api/src/procedures:
import { createActionEntity, createGameEntity } from '../entities/index.js';import { ActionSchema, IAction, QueryInputSchema, createPaginatedQueryOutput,} from '../schema/index.js';import { publicProcedure } from '../init.js';import { z } from 'zod';
export const queryActions = publicProcedure .input(QueryInputSchema.extend({ playerName: z.string() })) .output(createPaginatedQueryOutput(ActionSchema)) .query(async ({ input }) => { const actionEntity = createActionEntity(); const result = await actionEntity.query .primary({ playerName: input.playerName }) .go({ cursor: input.cursor, count: input.limit });
return { items: result.data as IAction[], cursor: result.cursor, }; });
export const saveAction = publicProcedure .input(ActionSchema.omit({ timestamp: true })) .output(ActionSchema) .mutation(async ({ input }) => { const actionEntity = createActionEntity(); const gameEntity = createGameEntity();
const action = await actionEntity.put(input).go(); await gameEntity .update({ playerName: input.playerName }) .set({ lastUpdated: action.data.timestamp }) .go(); return action.data as IAction; });import { createGameEntity } from '../entities/index.js';import { GameSchema, IGame, QueryInputSchema, createPaginatedQueryOutput,} from '../schema/index.js';import { publicProcedure } from '../init.js';
export const queryGames = publicProcedure .input(QueryInputSchema) .output(createPaginatedQueryOutput(GameSchema)) .query(async ({ input }) => { const gameEntity = createGameEntity(); const result = await gameEntity.scan.go({ cursor: input.cursor, count: input.limit, });
return { items: result.data as IGame[], cursor: result.cursor, }; });
export const saveGame = publicProcedure .input(GameSchema.omit({ lastUpdated: true })) .output(GameSchema) .mutation(async ({ input }) => { const gameEntity = createGameEntity();
const result = await gameEntity.put(input).go(); return result.data as IGame; });import { ItemSchema, QueryInputSchema, createPaginatedQueryOutput,} from '../schema/index.js';import { publicProcedure } from '../init.js';import { z } from 'zod';import { createInventoryEntity } from '../entities/index.js';
export const queryInventory = publicProcedure .input(QueryInputSchema.extend({ playerName: z.string() })) .output(createPaginatedQueryOutput(ItemSchema)) .query(async ({ input }) => { const inventoryEntity = createInventoryEntity(); const result = await inventoryEntity.query .primary({ playerName: input.playerName }) .go({ cursor: input.cursor, count: input.limit });
return { items: result.data, cursor: result.cursor, }; });Elimina il file echo.ts (da packages/game-api/src/procedures) poiché non lo utilizzeremo in questo progetto.
Configurazione del router
Sezione intitolata “Configurazione del router”Dopo aver definito le nostre procedure, per collegarle alla nostra API, aggiorna il seguente file:
import { t } from './init.js';import { queryActions, saveAction } from './procedures/actions.js';import { queryGames, saveGame } from './procedures/games.js';import { queryInventory } from './procedures/inventory.js';
export const router = t.router;
export const appRouter = router({ actions: router({ query: queryActions, save: saveAction, }), games: router({ query: queryGames, save: saveGame, }), inventory: router({ query: queryInventory, }),});
export type AppRouter = typeof appRouter;import { echo } from './procedures/echo.js';import { t } from './init.js';import { queryActions, saveAction } from './procedures/actions.js';import { queryGames, saveGame } from './procedures/games.js';import { queryInventory } from './procedures/inventory.js';
export const router = t.router;
export const appRouter = router({ echo, actions: router({ query: queryActions, save: saveAction, }), games: router({ query: queryGames, save: saveGame, }), inventory: router({ query: queryInventory, }),});
export type AppRouter = typeof appRouter;Task 2: Creare un server MCP per l’inventario
Sezione intitolata “Task 2: Creare un server MCP per l’inventario”Creiamo un server MCP che permetterà al nostro agente di gestire gli oggetti nell’inventario di un giocatore.
Definiremo i seguenti strumenti per il nostro agente:
list-inventory-itemsper recuperare gli oggetti correnti nell’inventario del giocatoreadd-to-inventoryper aggiungere oggetti all’inventario del giocatoreremove-from-inventoryper rimuovere oggetti dall’inventario del giocatore
Per risparmiare tempo, definiremo tutti gli strumenti inline:
import { McpServer } from '@modelcontextprotocol/sdk/server/mcp.js';import z from 'zod';import { createInventoryEntity } from ':dungeon-adventure/game-api';
/** * Create the MCP Server */export const createServer = () => { const server = new McpServer({ name: 'inventory-mcp-server', version: '1.0.0', });
const inventory = createInventoryEntity();
server.registerTool( 'list-inventory-items', { description: "List items in the player's inventory. Leave cursor blank unless you are requesting subsequent pages", inputSchema: { playerName: z.string(), cursor: z.string().optional(), }, }, async ({ playerName }) => { const results = await inventory.query .primary({ playerName, }) .go();
return { content: [{ type: 'text' as const, text: JSON.stringify(results) }], }; }, );
server.registerTool( 'add-to-inventory', { description: "Add an item to the player's inventory. Quantity defaults to 1 if omitted.", inputSchema: { playerName: z.string(), itemName: z.string(), emoji: z.string(), quantity: z.number().optional().default(1), }, }, async ({ playerName, itemName, emoji, quantity = 1 }) => { await inventory .put({ playerName, itemName, quantity, emoji, }) .go();
return { content: [ { type: 'text' as const, text: `Added ${itemName} (x${quantity}) to inventory`, }, ], }; }, );
server.registerTool( 'remove-from-inventory', { description: "Remove an item from the player's inventory. If quantity is omitted, all items are removed.", inputSchema: { playerName: z.string(), itemName: z.string(), quantity: z.number().optional(), }, }, async ({ playerName, itemName, quantity }) => { // If quantity is omitted, remove the entire item if (quantity === undefined) { try { await inventory.delete({ playerName, itemName }).go(); return { content: [ { type: 'text' as const, text: `${itemName} removed from inventory.` }, ], }; } catch { return { content: [ { type: 'text' as const, text: `${itemName} not found in inventory` }, ], }; } }
// If quantity is specified, fetch current quantity and update const item = await inventory.get({ playerName, itemName }).go();
if (!item.data) { return { content: [ { type: 'text' as const, text: `${itemName} not found in inventory` }, ], }; }
const newQuantity = item.data.quantity - quantity;
if (newQuantity <= 0) { await inventory.delete({ playerName, itemName }).go(); return { content: [ { type: 'text' as const, text: `${itemName} removed from inventory.` }, ], }; }
await inventory .put({ playerName, itemName, quantity: newQuantity, emoji: item.data.emoji, }) .go();
return { content: [ { type: 'text' as const, text: `Removed ${itemName} (x${quantity}) from inventory. ${newQuantity} remaining.`, }, ], }; }, );
return server;};import { McpServer } from '@modelcontextprotocol/sdk/server/mcp.js';import { registerAddTool } from './tools/add.js';import { registerSampleGuidanceResource } from './resources/sample-guidance.js';import z from 'zod';import { createInventoryEntity } from ':dungeon-adventure/game-api';
/** * Create the MCP Server */export const createServer = () => { const server = new McpServer({ name: 'inventory-mcp-server', version: '1.0.0', });
registerAddTool(server); registerSampleGuidanceResource(server); const inventory = createInventoryEntity();
server.registerTool( 'list-inventory-items', { description: "List items in the player's inventory. Leave cursor blank unless you are requesting subsequent pages", inputSchema: { playerName: z.string(), cursor: z.string().optional(), }, }, async ({ playerName }) => { const results = await inventory.query .primary({ playerName, }) .go();
return { content: [{ type: 'text' as const, text: JSON.stringify(results) }], }; }, );
server.registerTool( 'add-to-inventory', { description: "Add an item to the player's inventory. Quantity defaults to 1 if omitted.", inputSchema: { playerName: z.string(), itemName: z.string(), emoji: z.string(), quantity: z.number().optional().default(1), }, }, async ({ playerName, itemName, emoji, quantity = 1 }) => { await inventory .put({ playerName, itemName, quantity, emoji, }) .go();
return { content: [ { type: 'text' as const, text: `Added ${itemName} (x${quantity}) to inventory`, }, ], }; }, );
server.registerTool( 'remove-from-inventory', { description: "Remove an item from the player's inventory. If quantity is omitted, all items are removed.", inputSchema: { playerName: z.string(), itemName: z.string(), quantity: z.number().optional(), }, }, async ({ playerName, itemName, quantity }) => { // If quantity is omitted, remove the entire item if (quantity === undefined) { try { await inventory.delete({ playerName, itemName }).go(); return { content: [ { type: 'text' as const, text: `${itemName} removed from inventory.` }, ], }; } catch { return { content: [ { type: 'text' as const, text: `${itemName} not found in inventory` }, ], }; } }
// If quantity is specified, fetch current quantity and update const item = await inventory.get({ playerName, itemName }).go();
if (!item.data) { return { content: [ { type: 'text' as const, text: `${itemName} not found in inventory` }, ], }; }
const newQuantity = item.data.quantity - quantity;
if (newQuantity <= 0) { await inventory.delete({ playerName, itemName }).go(); return { content: [ { type: 'text' as const, text: `${itemName} removed from inventory.` }, ], }; }
await inventory .put({ playerName, itemName, quantity: newQuantity, emoji: item.data.emoji, }) .go();
return { content: [ { type: 'text' as const, text: `Removed ${itemName} (x${quantity}) from inventory. ${newQuantity} remaining.`, }, ], }; }, );
return server;};Man mano che il numero di strumenti cresce, puoi eventualmente rifattorizzarli in file separati.
Elimina le directory tools e resources in packages/inventory/src/mcp-server poiché non verranno utilizzate.
Task 3: Aggiornare l’infrastruttura
Sezione intitolata “Task 3: Aggiornare l’infrastruttura”Il passo finale è aggiornare la nostra infrastruttura per creare la tabella DynamoDB e concedere i permessi per eseguire operazioni dalla Game API.
Per farlo, aggiorna packages/infra/src come segue:
import { CfnOutput } from 'aws-cdk-lib';import { AttributeType, BillingMode, ProjectionType, Table, TableProps,} from 'aws-cdk-lib/aws-dynamodb';import { Construct } from 'constructs';import { suppressRules } from ':dungeon-adventure/common-constructs';
export type ElectrodbDynamoTableProps = Omit< TableProps, 'partitionKey' | 'sortKey' | 'billingMode'>;
export class ElectrodbDynamoTable extends Table { constructor(scope: Construct, id: string, props?: ElectrodbDynamoTableProps) { super(scope, id, { partitionKey: { name: 'pk', type: AttributeType.STRING, }, sortKey: { name: 'sk', type: AttributeType.STRING, }, billingMode: BillingMode.PAY_PER_REQUEST, ...props, });
this.addGlobalSecondaryIndex({ indexName: 'gsi1pk-gsi1sk-index', partitionKey: { name: 'gsi1pk', type: AttributeType.STRING, }, sortKey: { name: 'gsi1sk', type: AttributeType.STRING, }, projectionType: ProjectionType.ALL, });
// Suppress checkov rules that expect a KMS customer managed key and backup to be enabled suppressRules(this, ['CKV_AWS_119', 'CKV_AWS_28'], 'No need for custom encryption or backup');
new CfnOutput(this, 'TableName', { value: this.tableName }); }}import { GameApi, GameUI, InventoryMcpServer, RuntimeConfig, StoryAgent, UserIdentity,} from ':dungeon-adventure/common-constructs';import { Stack, StackProps, CfnOutput } from 'aws-cdk-lib';import { PolicyStatement } from 'aws-cdk-lib/aws-iam';import { Construct } from 'constructs';import { ElectrodbDynamoTable } from '../constructs/electrodb-table.js';import { RuntimeAuthorizerConfiguration } from '@aws-cdk/aws-bedrock-agentcore-alpha';
export class ApplicationStack extends Stack { constructor(scope: Construct, id: string, props?: StackProps) { super(scope, id, props);
const userIdentity = new UserIdentity(this, 'UserIdentity');
const electroDbTable = new ElectrodbDynamoTable(this, 'ElectroDbTable');
const gameApi = new GameApi(this, 'GameApi', { integrations: GameApi.defaultIntegrations(this) .withDefaultOptions({ environment: { TABLE_NAME: electroDbTable.tableName, }, }) .build(), });
electroDbTable.grantReadData(gameApi.integrations['actions.query'].handler); electroDbTable.grantReadData(gameApi.integrations['games.query'].handler); electroDbTable.grantReadData(gameApi.integrations['inventory.query'].handler); electroDbTable.grantReadWriteData( gameApi.integrations['actions.save'].handler, ); electroDbTable.grantReadWriteData( gameApi.integrations['games.save'].handler, );
const { userPool, userPoolClient } = userIdentity;
const mcpServer = new InventoryMcpServer(this, 'InventoryMcpServer', { environmentVariables: { TABLE_NAME: electroDbTable.tableName, }, }); electroDbTable.grantReadWriteData(mcpServer.agentCoreRuntime);
// Use Cognito for user authentication with the agent const storyAgent = new StoryAgent(this, 'StoryAgent', { authorizerConfiguration: RuntimeAuthorizerConfiguration.usingCognito( userPool, [userPoolClient], ), environmentVariables: { INVENTORY_MCP_ARN: mcpServer.agentCoreRuntime.agentRuntimeArn, }, });
// Grant the agent access to bedrock models storyAgent.agentCoreRuntime.addToRolePolicy( new PolicyStatement({ actions: [ 'bedrock:InvokeModel', 'bedrock:InvokeModelWithResponseStream', ], // You can scope the below down to the specific models you use resources: [ 'arn:aws:bedrock:*:*:foundation-model/*', 'arn:aws:bedrock:*:*:inference-profile/*', ], }), );
// Add the Story Agent ARN to runtime-config.json so it can be referenced by the website RuntimeConfig.ensure(this).config.agentArn = storyAgent.agentCoreRuntime.agentRuntimeArn;
new CfnOutput(this, 'StoryAgentArn', { value: storyAgent.agentCoreRuntime.agentRuntimeArn, }); new CfnOutput(this, 'InventoryMcpArn', { value: mcpServer.agentCoreRuntime.agentRuntimeArn, });
// Grant the agent permissions to invoke our mcp server mcpServer.agentCoreRuntime.grantInvoke(storyAgent.agentCoreRuntime);
// Grant the authenticated role access to invoke the api gameApi.grantInvokeAccess(userIdentity.identityPool.authenticatedRole);
// Ensure this is instantiated last so our runtime-config.json can be automatically configured new GameUI(this, 'GameUI'); }}import { GameApi, GameUI, InventoryMcpServer, RuntimeConfig, StoryAgent, UserIdentity,} from ':dungeon-adventure/common-constructs';import { Stack, StackProps, CfnOutput } from 'aws-cdk-lib';import { PolicyStatement } from 'aws-cdk-lib/aws-iam';import { Construct } from 'constructs';import { ElectrodbDynamoTable } from '../constructs/electrodb-table.js';import { RuntimeAuthorizerConfiguration } from '@aws-cdk/aws-bedrock-agentcore-alpha';
export class ApplicationStack extends Stack { constructor(scope: Construct, id: string, props?: StackProps) { super(scope, id, props);
const userIdentity = new UserIdentity(this, 'UserIdentity');
const electroDbTable = new ElectrodbDynamoTable(this, 'ElectroDbTable');
const gameApi = new GameApi(this, 'GameApi', { integrations: GameApi.defaultIntegrations(this).build(), integrations: GameApi.defaultIntegrations(this) .withDefaultOptions({ environment: { TABLE_NAME: electroDbTable.tableName, }, }) .build(), });
electroDbTable.grantReadData(gameApi.integrations['actions.query'].handler); electroDbTable.grantReadData(gameApi.integrations['games.query'].handler); electroDbTable.grantReadData(gameApi.integrations['inventory.query'].handler); electroDbTable.grantReadWriteData( gameApi.integrations['actions.save'].handler, ); electroDbTable.grantReadWriteData( gameApi.integrations['games.save'].handler, );
const { userPool, userPoolClient } = userIdentity;
const mcpServer = new InventoryMcpServer(this, 'InventoryMcpServer'); const mcpServer = new InventoryMcpServer(this, 'InventoryMcpServer', { environmentVariables: { TABLE_NAME: electroDbTable.tableName, }, }); electroDbTable.grantReadWriteData(mcpServer.agentCoreRuntime);
// Use Cognito for user authentication with the agent const storyAgent = new StoryAgent(this, 'StoryAgent', { authorizerConfiguration: RuntimeAuthorizerConfiguration.usingCognito( userPool, [userPoolClient], ), environmentVariables: { INVENTORY_MCP_ARN: mcpServer.agentCoreRuntime.agentRuntimeArn, }, });
// Grant the agent access to bedrock models storyAgent.agentCoreRuntime.addToRolePolicy( new PolicyStatement({ actions: [ 'bedrock:InvokeModel', 'bedrock:InvokeModelWithResponseStream', ], // You can scope the below down to the specific models you use resources: [ 'arn:aws:bedrock:*:*:foundation-model/*', 'arn:aws:bedrock:*:*:inference-profile/*', ], }), );
// Add the Story Agent ARN to runtime-config.json so it can be referenced by the website RuntimeConfig.ensure(this).config.agentArn = storyAgent.agentCoreRuntime.agentRuntimeArn;
new CfnOutput(this, 'StoryAgentArn', { value: storyAgent.agentCoreRuntime.agentRuntimeArn, }); new CfnOutput(this, 'InventoryMcpArn', { value: mcpServer.agentCoreRuntime.agentRuntimeArn, });
// Grant the agent permissions to invoke our mcp server mcpServer.agentCoreRuntime.grantInvoke(storyAgent.agentCoreRuntime);
// Grant the authenticated role access to invoke the api gameApi.grantInvokeAccess(userIdentity.identityPool.authenticatedRole);
// Ensure this is instantiated last so our runtime-config.json can be automatically configured new GameUI(this, 'GameUI'); }}Task 4: Deployment e testing
Sezione intitolata “Task 4: Deployment e testing”Prima, correggi eventuali problemi di linting:
pnpm lintyarn lintnpm run lintbun lintPoi compila la codebase:
pnpm buildyarn buildnpm run buildbun buildDeployare l’applicazione
Sezione intitolata “Deployare l’applicazione”Per deployare la tua applicazione, esegui il seguente comando:
pnpm nx deploy infra "dungeon-adventure-infra-sandbox/*"yarn nx deploy infra "dungeon-adventure-infra-sandbox/*"npx nx deploy infra "dungeon-adventure-infra-sandbox/*"bunx nx deploy infra "dungeon-adventure-infra-sandbox/*"Il primo deployment richiederà circa 8 minuti. I deployment successivi richiederanno circa 2 minuti.
Una volta completato il deployment, vedrai output simili ai seguenti (alcuni valori sono stati oscurati):
dungeon-adventure-sandbox-Applicationdungeon-adventure-sandbox-Application: deploying... [2/2]
✅ dungeon-adventure-sandbox-Application
✨ Deployment time: 354s
Outputs:dungeon-adventure-sandbox-Application.ElectroDbTableTableNameXXX = dungeon-adventure-sandbox-Application-ElectroDbTableXXX-YYYdungeon-adventure-sandbox-Application.GameApiEndpointXXX = https://xxx.execute-api.region.amazonaws.com/prod/dungeon-adventure-sandbox-Application.GameUIDistributionDomainNameXXX = xxx.cloudfront.netdungeon-adventure-sandbox-Application.StoryApiEndpointXXX = https://xxx.execute-api.region.amazonaws.com/prod/dungeon-adventure-sandbox-Application.UserIdentityUserIdentityIdentityPoolIdXXX = region:xxxdungeon-adventure-sandbox-Application.UserIdentityUserIdentityUserPoolIdXXX = region_xxxTestare l’API
Sezione intitolata “Testare l’API”Puoi testare l’API in due modi:
- Avviando un’istanza locale del backend tRPC e invocando le API con
curl. - Chiamare l'API deployata utilizzando curl con sigv4 abilitato
Curl con Sigv4 abilitato
Puoi aggiungere il seguente script al tuo file
.bashrc(ed eseguiresourcesu di esso) oppure incollare quanto segue nello stesso terminale in cui desideri eseguire il comando.~/.bashrc acurl () {REGION=$1SERVICE=$2shift; shift;curl --aws-sigv4 "aws:amz:$REGION:$SERVICE" --user "$(aws configure get aws_access_key_id):$(aws configure get aws_secret_access_key)" -H "X-Amz-Security-Token: $(aws configure get aws_session_token)" "$@"}Per effettuare una richiesta curl autenticata con
sigv4, invocaacurlcome segue:Terminal window acurl <region> <service> <other-curl-arguments>Ad esempio:
API Gateway
Sezione intitolata “API Gateway”Terminal window acurl ap-southeast-2 execute-api -X GET https://xxxURL funzione Lambda streaming
Sezione intitolata “URL funzione Lambda streaming”Terminal window acurl ap-southeast-2 lambda -N -X POST https://xxxPuoi aggiungere la seguente funzione al tuo profilo PowerShell oppure incollare quanto segue nella stessa sessione PowerShell in cui desideri eseguire il comando.
Terminal window # PowerShell profile or current sessionfunction acurl {param([Parameter(Mandatory=$true)][string]$Region,[Parameter(Mandatory=$true)][string]$Service,[Parameter(ValueFromRemainingArguments=$true)][string[]]$CurlArgs)$AccessKey = aws configure get aws_access_key_id$SecretKey = aws configure get aws_secret_access_key$SessionToken = aws configure get aws_session_token& curl --aws-sigv4 "aws:amz:$Region`:$Service" --user "$AccessKey`:$SecretKey" -H "X-Amz-Security-Token: $SessionToken" @CurlArgs}Per effettuare una richiesta curl autenticata con
sigv4, invocaacurlutilizzando questi esempi:API Gateway
Sezione intitolata “API Gateway”Terminal window acurl ap-southeast-2 execute-api -X GET https://xxxURL funzione Lambda streaming
Sezione intitolata “URL funzione Lambda streaming”Terminal window acurl ap-southeast-2 lambda -N -X POST https://xxx
Per avviare il server locale game-api, esegui il seguente comando:
TABLE_NAME=dungeon-adventure-infra-sandbox-Application-ElectroDbTableXXX-YYY pnpm nx run @dungeon-adventure/game-api:serveTABLE_NAME=dungeon-adventure-infra-sandbox-Application-ElectroDbTableXXX-YYY yarn nx run @dungeon-adventure/game-api:serveTABLE_NAME=dungeon-adventure-infra-sandbox-Application-ElectroDbTableXXX-YYY npx nx run @dungeon-adventure/game-api:serveTABLE_NAME=dungeon-adventure-infra-sandbox-Application-ElectroDbTableXXX-YYY bunx nx run @dungeon-adventure/game-api:serveUna volta avviato il server, puoi chiamarlo eseguendo il seguente comando:
curl -X GET 'http://localhost:2022/games.query?input=%7B%7D'acurl ap-southeast-2 execute-api -X GET 'https://xxx.execute-api.ap-southeast-2.amazonaws.com/prod/games.query?input=%7B%7D'Se il comando viene eseguito con successo, vedrai una risposta come:
{"result":{"data":{"items":[],"cursor":null}}}Complimenti, hai costruito e deployato la tua prima API utilizzando tRPC! 🎉🎉🎉