Connecting To Redshift
Orbit team(s) get AWS Redshift cluster interaction capability using Orbit Redshift plugin. Please refer to plugin-library more details about addition of plugin to team deployment.
To interact with the Redshift cluster(s), Orbit SDK provides abstracted helper functions over AWS Boto3 calls, which are further integrated with Orbit JupyterLab iPython magic commands.
Below explain the various ways the Orbit Workbench allows team user(s) to interact with AWS Redshift cluster(s).
iPython Magic based creating, connection and destroying
Connect to an existing cluster or create a new cluster if it does not exists.
>>> %connect_to_redshift -cluster db-test -reuse -start -func Standard Nodes=3
Parameters
'-cluster' : str Specify cluster name
'-start' : bool, optional Start cluster if it does not exists (default False)
'-reuse' : bool, optional Reuse cluster if cluster name exists (default True)
'-func' : str, optional String based options parsing.
First parameter - Standard or custom lambda name postfix
Standard - Default orbit lambda used to create and connect to cluster.
custom lambda name postfix - Used to create a custom redshift cluster.
Remaining parameters specific to redshift arguments(e.g. Nodes, max_concurrency_scaling_clusters, etc.)(default None).
Note - Per Orbit resource naming standards, the redshift cluster name created will be of below format.
cluster_identifier = f"orbit-{env}-{team_space}-{cluster_name}".lower()
Delete an existing Redshift cluster
>>> %delete_redshift_cluster -cluster db-test
Parameters
'-cluster' : str Specify cluster name
Using Orbit SDK calls.
Connect to a Redshift Cluster and return connection information once redshift cluster is available for use.
>>> from aws.utils.notebooks.database import RedshiftUtils
>>> from aws.utils.notebooks.common import get_properties
>>> response = RedshiftUtils.connect_to_redshift(cluster_name= 'cluster-test')
>>> print(response)
{
"db_url": <redshift+psycopg2://..>,
"engine": <engine>,
"cluster_identifier": <cluster name>,
"started": <started>,
"redshift_role": <'arn:aws:iam::{accountid}:role/...'>,
}
Parameters
cluster_name : str Name of the redshift cluster
reuseCluster : bool, optional Boolean determining if you wish to reuse an existing cluster name (default True).
startCluster : bool, optional Boolean determining if you wish to start a new cluster (default False)
clusterArgs : dict(), optional Other redshift parameters you can optionally specify (e.g. auto_analyze, max_concurrency_scaling_clusters, statement_timeout, etc.)
Returns
db_url : str A sqlalchemy connection string
engine: sqlalchemy.engine.Engine A sql alchemy engine
cluster_identifier: str The unique identifier of the cluster
started: bool Boolean representing if cluster has started or not
redshift_role: str The redshift role ARN that can be used to access other AWS services when you execute the Amazon Redshift command
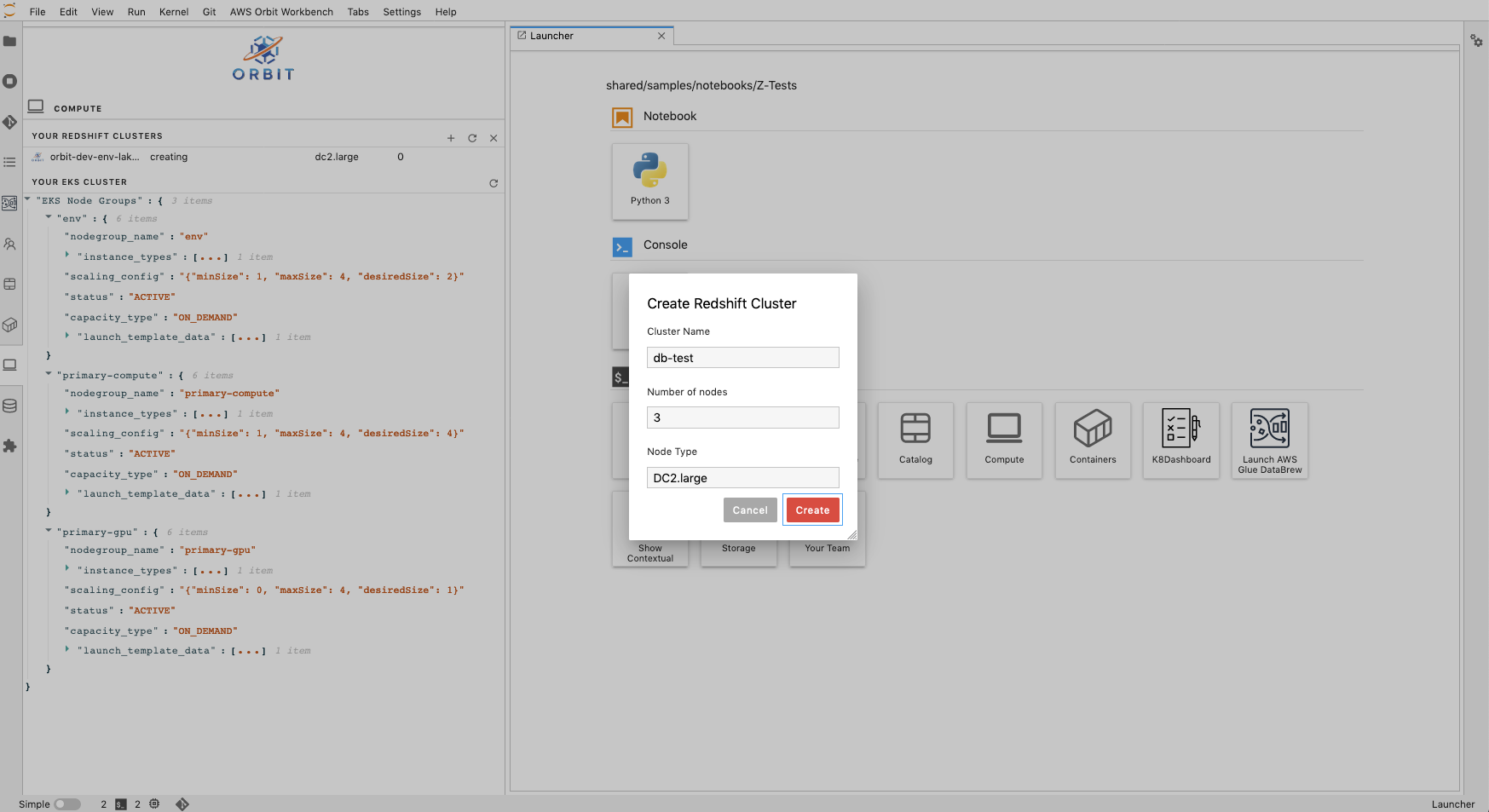
JL UI based creating and destroying cluster.
The JupyterLab UI has Compute section holding Redshift cluster display list, creation and deletion buttons. Below screenshot displays the model dialog requesting for cluster name, number of nodes and node type.
Click “+” icon to create new cluster. By selecting existing cluster in the list, click ‘x’ icon to delete the cluster.