Implémenter l'API de Jeu et le serveur MCP d'Inventaire
Tâche 1 : Implémenter l’API de jeu
Section intitulée « Tâche 1 : Implémenter l’API de jeu »Nous allons implémenter les API suivantes dans cette section :
saveGame- créer ou mettre à jour une partie.queryGames- retourner une liste paginée des parties précédemment sauvegardées.saveAction- sauvegarder une action pour une partie donnée.queryActions- retourner une liste paginée de toutes les actions liées à une partie.queryInventory- retourner une liste paginée des objets dans l’inventaire d’un joueur.
Schéma d’API
Section intitulée « Schéma d’API »Pour définir les entrées et sorties de notre API, créons notre schéma avec Zod dans le fichier packages/game-api/src/schema/index.ts comme suit :
import { z } from 'zod';
export const QueryInputSchema = z.object({ cursor: z.string().optional(), limit: z.number().optional().default(100),});export type IQueryInput = z.TypeOf<typeof QueryInputSchema>;
export const ActionSchema = z.object({ playerName: z.string(), timestamp: z.iso.datetime(), role: z.enum(['assistant', 'user']), content: z.string(),});export type IAction = z.TypeOf<typeof ActionSchema>;
export const GameSchema = z.object({ playerName: z.string(), genre: z.enum(['zombie', 'superhero', 'medieval']), lastUpdated: z.iso.datetime(),});export type IGame = z.TypeOf<typeof GameSchema>;
export const ItemSchema = z.object({ playerName: z.string(), itemName: z.string(), emoji: z.string().optional(), lastUpdated: z.iso.datetime(), quantity: z.number(),});export type IItem = z.TypeOf<typeof ItemSchema>;
export const createPaginatedQueryOutput = <ItemType extends z.ZodTypeAny>( itemSchema: ItemType,) => { return z.object({ items: z.array(itemSchema), cursor: z.string().nullable(), });};export * from './echo.js'import { z } from 'zod';
export const QueryInputSchema = z.object({ cursor: z.string().optional(), limit: z.number().optional().default(100),});export type IQueryInput = z.TypeOf<typeof QueryInputSchema>;
export const ActionSchema = z.object({ playerName: z.string(), timestamp: z.iso.datetime(), role: z.enum(['assistant', 'user']), content: z.string(),});export type IAction = z.TypeOf<typeof ActionSchema>;
export const GameSchema = z.object({ playerName: z.string(), genre: z.enum(['zombie', 'superhero', 'medieval']), lastUpdated: z.iso.datetime(),});export type IGame = z.TypeOf<typeof GameSchema>;
export const ItemSchema = z.object({ playerName: z.string(), itemName: z.string(), emoji: z.string().optional(), lastUpdated: z.iso.datetime(), quantity: z.number(),});export type IItem = z.TypeOf<typeof ItemSchema>;
export const createPaginatedQueryOutput = <ItemType extends z.ZodTypeAny>( itemSchema: ItemType,) => { return z.object({ items: z.array(itemSchema), cursor: z.string().nullable(), });};Supprimez le fichier packages/game-api/src/schema/echo.ts car nous ne l’utiliserons pas dans ce projet.
Modélisation des entités
Section intitulée « Modélisation des entités »Voici le diagramme entité-relation de notre application.
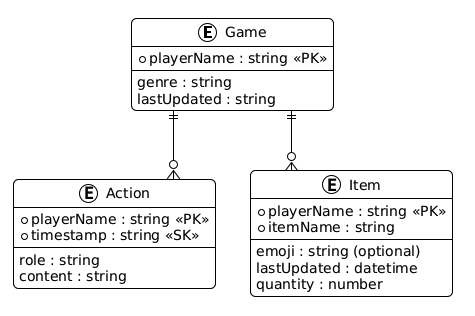
Nous allons implémenter notre base de données dans DynamoDB en utilisant la bibliothèque cliente ElectroDB pour simplifier les choses. Pour installer electrodb et le client DynamoDB, exécutez cette commande :
pnpm add -w electrodb@3.5.3 @aws-sdk/client-dynamodb@3.992.0yarn add electrodb@3.5.3 @aws-sdk/client-dynamodb@3.992.0npm install --legacy-peer-deps electrodb@3.5.3 @aws-sdk/client-dynamodb@3.992.0bun install electrodb@3.5.3 @aws-sdk/client-dynamodb@3.992.0Pour définir nos entités ElectroDB à partir du diagramme ER, créons le fichier packages/game-api/src/entities/index.ts :
import { Entity } from 'electrodb';import { DynamoDBClient } from '@aws-sdk/client-dynamodb';
export const createActionEntity = (client: DynamoDBClient = new DynamoDBClient()) => new Entity( { model: { entity: 'Action', version: '1', service: 'game', }, attributes: { playerName: { type: 'string', required: true, readOnly: true }, timestamp: { type: 'string', required: true, readOnly: true, set: () => new Date().toISOString(), default: () => new Date().toISOString(), }, role: { type: 'string', required: true, readOnly: true }, content: { type: 'string', required: true, readOnly: true }, }, indexes: { primary: { pk: { field: 'pk', composite: ['playerName'] }, sk: { field: 'sk', composite: ['timestamp'] }, }, }, }, { client, table: process.env.TABLE_NAME }, );
export const createGameEntity = (client: DynamoDBClient = new DynamoDBClient()) => new Entity( { model: { entity: 'Game', version: '1', service: 'game', }, attributes: { playerName: { type: 'string', required: true, readOnly: true }, genre: { type: 'string', required: true, readOnly: true }, lastUpdated: { type: 'string', required: true, default: () => new Date().toISOString(), }, }, indexes: { primary: { pk: { field: 'pk', composite: ['playerName'] }, sk: { field: 'sk', composite: [], }, }, }, }, { client, table: process.env.TABLE_NAME }, );
export const createInventoryEntity = (client: DynamoDBClient = new DynamoDBClient()) => new Entity( { model: { entity: 'Inventory', version: '1', service: 'game', }, attributes: { playerName: { type: 'string', required: true, readOnly: true }, lastUpdated: { type: 'string', required: true, default: () => new Date().toISOString(), }, itemName: { type: 'string', required: true, }, emoji: { type: 'string', required: false, }, quantity: { type: 'number', required: true, }, }, indexes: { primary: { pk: { field: 'pk', composite: ['playerName'] }, sk: { field: 'sk', composite: ['itemName'] }, }, }, }, { client, table: process.env.TABLE_NAME }, );ElectroDB nous permet non seulement de définir nos types, mais aussi de fournir des valeurs par défaut pour certains champs comme les horodatages. De plus, ElectroDB suit le single-table design, une meilleure pratique avec DynamoDB.
Pour préparer l’interaction du serveur MCP avec l’inventaire, assurons-nous d’exporter l’entité d’inventaire dans packages/game-api/src/index.ts :
export type { AppRouter } from './router.js';export { appRouter } from './router.js';export type { Context } from './init.js';export * from './client/index.js';export * from './schema/index.js';export * from './entities/index.js';Définition des procédures
Section intitulée « Définition des procédures »Pour implémenter les méthodes de l’API, effectuez les modifications suivantes dans packages/game-api/src/procedures :
import { createActionEntity, createGameEntity } from '../entities/index.js';import { ActionSchema, IAction, QueryInputSchema, createPaginatedQueryOutput,} from '../schema/index.js';import { publicProcedure } from '../init.js';import { z } from 'zod';
export const queryActions = publicProcedure .input(QueryInputSchema.extend({ playerName: z.string() })) .output(createPaginatedQueryOutput(ActionSchema)) .query(async ({ input }) => { const actionEntity = createActionEntity(); const result = await actionEntity.query .primary({ playerName: input.playerName }) .go({ cursor: input.cursor, count: input.limit });
return { items: result.data as IAction[], cursor: result.cursor, }; });
export const saveAction = publicProcedure .input(ActionSchema.omit({ timestamp: true })) .output(ActionSchema) .mutation(async ({ input }) => { const actionEntity = createActionEntity(); const gameEntity = createGameEntity();
const action = await actionEntity.put(input).go(); await gameEntity .update({ playerName: input.playerName }) .set({ lastUpdated: action.data.timestamp }) .go(); return action.data as IAction; });import { createGameEntity } from '../entities/index.js';import { GameSchema, IGame, QueryInputSchema, createPaginatedQueryOutput,} from '../schema/index.js';import { publicProcedure } from '../init.js';
export const queryGames = publicProcedure .input(QueryInputSchema) .output(createPaginatedQueryOutput(GameSchema)) .query(async ({ input }) => { const gameEntity = createGameEntity(); const result = await gameEntity.scan.go({ cursor: input.cursor, count: input.limit, });
return { items: result.data as IGame[], cursor: result.cursor, }; });
export const saveGame = publicProcedure .input(GameSchema.omit({ lastUpdated: true })) .output(GameSchema) .mutation(async ({ input }) => { const gameEntity = createGameEntity();
const result = await gameEntity.put(input).go(); return result.data as IGame; });import { ItemSchema, QueryInputSchema, createPaginatedQueryOutput,} from '../schema/index.js';import { publicProcedure } from '../init.js';import { z } from 'zod';import { createInventoryEntity } from '../entities/index.js';
export const queryInventory = publicProcedure .input(QueryInputSchema.extend({ playerName: z.string() })) .output(createPaginatedQueryOutput(ItemSchema)) .query(async ({ input }) => { const inventoryEntity = createInventoryEntity(); const result = await inventoryEntity.query .primary({ playerName: input.playerName }) .go({ cursor: input.cursor, count: input.limit });
return { items: result.data, cursor: result.cursor, }; });Supprimez le fichier echo.ts (dans packages/game-api/src/procedures) car nous ne l’utiliserons pas dans ce projet.
Configuration du routeur
Section intitulée « Configuration du routeur »Après avoir défini nos procédures, pour les connecter à notre API, modifiez le fichier suivant :
import { t } from './init.js';import { queryActions, saveAction } from './procedures/actions.js';import { queryGames, saveGame } from './procedures/games.js';import { queryInventory } from './procedures/inventory.js';
export const router = t.router;
export const appRouter = router({ actions: router({ query: queryActions, save: saveAction, }), games: router({ query: queryGames, save: saveGame, }), inventory: router({ query: queryInventory, }),});
export type AppRouter = typeof appRouter;import { echo } from './procedures/echo.js';import { t } from './init.js';import { queryActions, saveAction } from './procedures/actions.js';import { queryGames, saveGame } from './procedures/games.js';import { queryInventory } from './procedures/inventory.js';
export const router = t.router;
export const appRouter = router({ echo, actions: router({ query: queryActions, save: saveAction, }), games: router({ query: queryGames, save: saveGame, }), inventory: router({ query: queryInventory, }),});
export type AppRouter = typeof appRouter;Tâche 2 : Créer un serveur MCP d’inventaire
Section intitulée « Tâche 2 : Créer un serveur MCP d’inventaire »Créons maintenant un serveur MCP permettant à notre agent de gérer l’inventaire des joueurs.
Nous définirons les outils suivants pour notre agent :
list-inventory-itemspour récupérer les objets actuels de l’inventaireadd-to-inventorypour ajouter des objets à l’inventaireremove-from-inventorypour retirer des objets de l’inventaire
Pour gagner du temps, nous définirons tous les outils inline :
import { McpServer } from '@modelcontextprotocol/sdk/server/mcp.js';import z from 'zod';import { createInventoryEntity } from ':dungeon-adventure/game-api';
/** * Create the MCP Server */export const createServer = () => { const server = new McpServer({ name: 'inventory-mcp-server', version: '1.0.0', });
const inventory = createInventoryEntity();
server.registerTool( 'list-inventory-items', { description: "List items in the player's inventory. Leave cursor blank unless you are requesting subsequent pages", inputSchema: { playerName: z.string(), cursor: z.string().optional(), }, }, async ({ playerName }) => { const results = await inventory.query .primary({ playerName, }) .go();
return { content: [{ type: 'text' as const, text: JSON.stringify(results) }], }; }, );
server.registerTool( 'add-to-inventory', { description: "Add an item to the player's inventory. Quantity defaults to 1 if omitted.", inputSchema: { playerName: z.string(), itemName: z.string(), emoji: z.string(), quantity: z.number().optional().default(1), }, }, async ({ playerName, itemName, emoji, quantity = 1 }) => { await inventory .put({ playerName, itemName, quantity, emoji, }) .go();
return { content: [ { type: 'text' as const, text: `Added ${itemName} (x${quantity}) to inventory`, }, ], }; }, );
server.registerTool( 'remove-from-inventory', { description: "Remove an item from the player's inventory. If quantity is omitted, all items are removed.", inputSchema: { playerName: z.string(), itemName: z.string(), quantity: z.number().optional(), }, }, async ({ playerName, itemName, quantity }) => { // If quantity is omitted, remove the entire item if (quantity === undefined) { try { await inventory.delete({ playerName, itemName }).go(); return { content: [ { type: 'text' as const, text: `${itemName} removed from inventory.` }, ], }; } catch { return { content: [ { type: 'text' as const, text: `${itemName} not found in inventory` }, ], }; } }
// If quantity is specified, fetch current quantity and update const item = await inventory.get({ playerName, itemName }).go();
if (!item.data) { return { content: [ { type: 'text' as const, text: `${itemName} not found in inventory` }, ], }; }
const newQuantity = item.data.quantity - quantity;
if (newQuantity <= 0) { await inventory.delete({ playerName, itemName }).go(); return { content: [ { type: 'text' as const, text: `${itemName} removed from inventory.` }, ], }; }
await inventory .put({ playerName, itemName, quantity: newQuantity, emoji: item.data.emoji, }) .go();
return { content: [ { type: 'text' as const, text: `Removed ${itemName} (x${quantity}) from inventory. ${newQuantity} remaining.`, }, ], }; }, );
return server;};import { McpServer } from '@modelcontextprotocol/sdk/server/mcp.js';import { registerAddTool } from './tools/add.js';import { registerSampleGuidanceResource } from './resources/sample-guidance.js';import z from 'zod';import { createInventoryEntity } from ':dungeon-adventure/game-api';
/** * Create the MCP Server */export const createServer = () => { const server = new McpServer({ name: 'inventory-mcp-server', version: '1.0.0', });
registerAddTool(server); registerSampleGuidanceResource(server); const inventory = createInventoryEntity();
server.registerTool( 'list-inventory-items', { description: "List items in the player's inventory. Leave cursor blank unless you are requesting subsequent pages", inputSchema: { playerName: z.string(), cursor: z.string().optional(), }, }, async ({ playerName }) => { const results = await inventory.query .primary({ playerName, }) .go();
return { content: [{ type: 'text' as const, text: JSON.stringify(results) }], }; }, );
server.registerTool( 'add-to-inventory', { description: "Add an item to the player's inventory. Quantity defaults to 1 if omitted.", inputSchema: { playerName: z.string(), itemName: z.string(), emoji: z.string(), quantity: z.number().optional().default(1), }, }, async ({ playerName, itemName, emoji, quantity = 1 }) => { await inventory .put({ playerName, itemName, quantity, emoji, }) .go();
return { content: [ { type: 'text' as const, text: `Added ${itemName} (x${quantity}) to inventory`, }, ], }; }, );
server.registerTool( 'remove-from-inventory', { description: "Remove an item from the player's inventory. If quantity is omitted, all items are removed.", inputSchema: { playerName: z.string(), itemName: z.string(), quantity: z.number().optional(), }, }, async ({ playerName, itemName, quantity }) => { // If quantity is omitted, remove the entire item if (quantity === undefined) { try { await inventory.delete({ playerName, itemName }).go(); return { content: [ { type: 'text' as const, text: `${itemName} removed from inventory.` }, ], }; } catch { return { content: [ { type: 'text' as const, text: `${itemName} not found in inventory` }, ], }; } }
// If quantity is specified, fetch current quantity and update const item = await inventory.get({ playerName, itemName }).go();
if (!item.data) { return { content: [ { type: 'text' as const, text: `${itemName} not found in inventory` }, ], }; }
const newQuantity = item.data.quantity - quantity;
if (newQuantity <= 0) { await inventory.delete({ playerName, itemName }).go(); return { content: [ { type: 'text' as const, text: `${itemName} removed from inventory.` }, ], }; }
await inventory .put({ playerName, itemName, quantity: newQuantity, emoji: item.data.emoji, }) .go();
return { content: [ { type: 'text' as const, text: `Removed ${itemName} (x${quantity}) from inventory. ${newQuantity} remaining.`, }, ], }; }, );
return server;};Si le nombre d’outils augmente, vous pourrez les refactoriser dans des fichiers séparés si vous le souhaitez.
Supprimez les répertoires tools et resources dans packages/inventory/src/mcp-server car ils ne seront pas utilisés.
Tâche 3 : Mettre à jour l’infrastructure
Section intitulée « Tâche 3 : Mettre à jour l’infrastructure »La dernière étape consiste à mettre à jour notre infrastructure pour créer la table DynamoDB et accorder les permissions nécessaires à l’API de jeu.
Pour ce faire, modifiez packages/infra/src comme suit :
import { CfnOutput } from 'aws-cdk-lib';import { AttributeType, BillingMode, ProjectionType, Table, TableProps,} from 'aws-cdk-lib/aws-dynamodb';import { Construct } from 'constructs';import { suppressRules } from ':dungeon-adventure/common-constructs';
export type ElectrodbDynamoTableProps = Omit< TableProps, 'partitionKey' | 'sortKey' | 'billingMode'>;
export class ElectrodbDynamoTable extends Table { constructor(scope: Construct, id: string, props?: ElectrodbDynamoTableProps) { super(scope, id, { partitionKey: { name: 'pk', type: AttributeType.STRING, }, sortKey: { name: 'sk', type: AttributeType.STRING, }, billingMode: BillingMode.PAY_PER_REQUEST, ...props, });
this.addGlobalSecondaryIndex({ indexName: 'gsi1pk-gsi1sk-index', partitionKey: { name: 'gsi1pk', type: AttributeType.STRING, }, sortKey: { name: 'gsi1sk', type: AttributeType.STRING, }, projectionType: ProjectionType.ALL, });
// Suppress checkov rules that expect a KMS customer managed key and backup to be enabled suppressRules(this, ['CKV_AWS_119', 'CKV_AWS_28'], 'No need for custom encryption or backup');
new CfnOutput(this, 'TableName', { value: this.tableName }); }}import { GameApi, GameUI, InventoryMcpServer, RuntimeConfig, StoryAgent, UserIdentity,} from ':dungeon-adventure/common-constructs';import { Stack, StackProps, CfnOutput } from 'aws-cdk-lib';import { PolicyStatement } from 'aws-cdk-lib/aws-iam';import { Construct } from 'constructs';import { ElectrodbDynamoTable } from '../constructs/electrodb-table.js';import { RuntimeAuthorizerConfiguration } from '@aws-cdk/aws-bedrock-agentcore-alpha';
export class ApplicationStack extends Stack { constructor(scope: Construct, id: string, props?: StackProps) { super(scope, id, props);
const userIdentity = new UserIdentity(this, 'UserIdentity');
const electroDbTable = new ElectrodbDynamoTable(this, 'ElectroDbTable');
const gameApi = new GameApi(this, 'GameApi', { integrations: GameApi.defaultIntegrations(this) .withDefaultOptions({ environment: { TABLE_NAME: electroDbTable.tableName, }, }) .build(), });
electroDbTable.grantReadData(gameApi.integrations['actions.query'].handler); electroDbTable.grantReadData(gameApi.integrations['games.query'].handler); electroDbTable.grantReadData(gameApi.integrations['inventory.query'].handler); electroDbTable.grantReadWriteData( gameApi.integrations['actions.save'].handler, ); electroDbTable.grantReadWriteData( gameApi.integrations['games.save'].handler, );
const { userPool, userPoolClient } = userIdentity;
const mcpServer = new InventoryMcpServer(this, 'InventoryMcpServer', { environmentVariables: { TABLE_NAME: electroDbTable.tableName, }, }); electroDbTable.grantReadWriteData(mcpServer.agentCoreRuntime);
// Use Cognito for user authentication with the agent const storyAgent = new StoryAgent(this, 'StoryAgent', { authorizerConfiguration: RuntimeAuthorizerConfiguration.usingCognito( userPool, [userPoolClient], ), environmentVariables: { INVENTORY_MCP_ARN: mcpServer.agentCoreRuntime.agentRuntimeArn, }, });
// Grant the agent access to bedrock models storyAgent.agentCoreRuntime.addToRolePolicy( new PolicyStatement({ actions: [ 'bedrock:InvokeModel', 'bedrock:InvokeModelWithResponseStream', ], // You can scope the below down to the specific models you use resources: [ 'arn:aws:bedrock:*:*:foundation-model/*', 'arn:aws:bedrock:*:*:inference-profile/*', ], }), );
// Add the Story Agent ARN to runtime-config.json so it can be referenced by the website RuntimeConfig.ensure(this).config.agentArn = storyAgent.agentCoreRuntime.agentRuntimeArn;
new CfnOutput(this, 'StoryAgentArn', { value: storyAgent.agentCoreRuntime.agentRuntimeArn, }); new CfnOutput(this, 'InventoryMcpArn', { value: mcpServer.agentCoreRuntime.agentRuntimeArn, });
// Grant the agent permissions to invoke our mcp server mcpServer.agentCoreRuntime.grantInvoke(storyAgent.agentCoreRuntime);
// Grant the authenticated role access to invoke the api gameApi.grantInvokeAccess(userIdentity.identityPool.authenticatedRole);
// Ensure this is instantiated last so our runtime-config.json can be automatically configured new GameUI(this, 'GameUI'); }}import { GameApi, GameUI, InventoryMcpServer, RuntimeConfig, StoryAgent, UserIdentity,} from ':dungeon-adventure/common-constructs';import { Stack, StackProps, CfnOutput } from 'aws-cdk-lib';import { PolicyStatement } from 'aws-cdk-lib/aws-iam';import { Construct } from 'constructs';import { ElectrodbDynamoTable } from '../constructs/electrodb-table.js';import { RuntimeAuthorizerConfiguration } from '@aws-cdk/aws-bedrock-agentcore-alpha';
export class ApplicationStack extends Stack { constructor(scope: Construct, id: string, props?: StackProps) { super(scope, id, props);
const userIdentity = new UserIdentity(this, 'UserIdentity');
const electroDbTable = new ElectrodbDynamoTable(this, 'ElectroDbTable');
const gameApi = new GameApi(this, 'GameApi', { integrations: GameApi.defaultIntegrations(this).build(), integrations: GameApi.defaultIntegrations(this) .withDefaultOptions({ environment: { TABLE_NAME: electroDbTable.tableName, }, }) .build(), });
electroDbTable.grantReadData(gameApi.integrations['actions.query'].handler); electroDbTable.grantReadData(gameApi.integrations['games.query'].handler); electroDbTable.grantReadData(gameApi.integrations['inventory.query'].handler); electroDbTable.grantReadWriteData( gameApi.integrations['actions.save'].handler, ); electroDbTable.grantReadWriteData( gameApi.integrations['games.save'].handler, );
const { userPool, userPoolClient } = userIdentity;
const mcpServer = new InventoryMcpServer(this, 'InventoryMcpServer'); const mcpServer = new InventoryMcpServer(this, 'InventoryMcpServer', { environmentVariables: { TABLE_NAME: electroDbTable.tableName, }, }); electroDbTable.grantReadWriteData(mcpServer.agentCoreRuntime);
// Use Cognito for user authentication with the agent const storyAgent = new StoryAgent(this, 'StoryAgent', { authorizerConfiguration: RuntimeAuthorizerConfiguration.usingCognito( userPool, [userPoolClient], ), environmentVariables: { INVENTORY_MCP_ARN: mcpServer.agentCoreRuntime.agentRuntimeArn, }, });
// Grant the agent access to bedrock models storyAgent.agentCoreRuntime.addToRolePolicy( new PolicyStatement({ actions: [ 'bedrock:InvokeModel', 'bedrock:InvokeModelWithResponseStream', ], // You can scope the below down to the specific models you use resources: [ 'arn:aws:bedrock:*:*:foundation-model/*', 'arn:aws:bedrock:*:*:inference-profile/*', ], }), );
// Add the Story Agent ARN to runtime-config.json so it can be referenced by the website RuntimeConfig.ensure(this).config.agentArn = storyAgent.agentCoreRuntime.agentRuntimeArn;
new CfnOutput(this, 'StoryAgentArn', { value: storyAgent.agentCoreRuntime.agentRuntimeArn, }); new CfnOutput(this, 'InventoryMcpArn', { value: mcpServer.agentCoreRuntime.agentRuntimeArn, });
// Grant the agent permissions to invoke our mcp server mcpServer.agentCoreRuntime.grantInvoke(storyAgent.agentCoreRuntime);
// Grant the authenticated role access to invoke the api gameApi.grantInvokeAccess(userIdentity.identityPool.authenticatedRole);
// Ensure this is instantiated last so our runtime-config.json can be automatically configured new GameUI(this, 'GameUI'); }}Tâche 4 : Déploiement et tests
Section intitulée « Tâche 4 : Déploiement et tests »Tout d’abord, corrigez les problèmes de lint :
pnpm lintyarn lintnpm run lintbun lintPuis compilez le codebase :
pnpm buildyarn buildnpm run buildbun buildDéployer votre application
Section intitulée « Déployer votre application »Pour déployer votre application, exécutez la commande suivante :
pnpm nx deploy infra "dungeon-adventure-infra-sandbox/*"yarn nx deploy infra "dungeon-adventure-infra-sandbox/*"npx nx deploy infra "dungeon-adventure-infra-sandbox/*"bunx nx deploy infra "dungeon-adventure-infra-sandbox/*"Le premier déploiement prendra environ 8 minutes. Les déploiements suivants prendront environ 2 minutes.
Une fois le déploiement terminé, vous verrez des sorties similaires à ceci (certaines valeurs ont été masquées) :
dungeon-adventure-sandbox-Applicationdungeon-adventure-sandbox-Application: deploying... [2/2]
✅ dungeon-adventure-sandbox-Application
✨ Deployment time: 354s
Outputs:dungeon-adventure-sandbox-Application.ElectroDbTableTableNameXXX = dungeon-adventure-sandbox-Application-ElectroDbTableXXX-YYYdungeon-adventure-sandbox-Application.GameApiEndpointXXX = https://xxx.execute-api.region.amazonaws.com/prod/dungeon-adventure-sandbox-Application.GameUIDistributionDomainNameXXX = xxx.cloudfront.netdungeon-adventure-sandbox-Application.StoryApiEndpointXXX = https://xxx.execute-api.region.amazonaws.com/prod/dungeon-adventure-sandbox-Application.UserIdentityUserIdentityIdentityPoolIdXXX = region:xxxdungeon-adventure-sandbox-Application.UserIdentityUserIdentityUserPoolIdXXX = region_xxxTester l’API
Section intitulée « Tester l’API »Vous pouvez tester l’API via :
- Le démarrage d’une instance locale du backend tRPC et l’invocation des API avec
curl. - Appeler l'API déployée avec curl sigv4
curl avec Sigv4
Vous pouvez soit ajouter le script suivant à votre fichier
.bashrc(et lesource), soit coller ce qui suit dans le même terminal dans lequel vous souhaitez exécuter la commande.~/.bashrc acurl () {REGION=$1SERVICE=$2shift; shift;curl --aws-sigv4 "aws:amz:$REGION:$SERVICE" --user "$(aws configure get aws_access_key_id):$(aws configure get aws_secret_access_key)" -H "X-Amz-Security-Token: $(aws configure get aws_session_token)" "$@"}Pour effectuer une requête curl authentifiée
sigv4, invoquezacurlcomme suit :Fenêtre de terminal acurl <region> <service> <other-curl-arguments>Par exemple :
API Gateway
Section intitulée « API Gateway »Fenêtre de terminal acurl ap-southeast-2 execute-api -X GET https://xxxURL de fonction Lambda en streaming
Section intitulée « URL de fonction Lambda en streaming »Fenêtre de terminal acurl ap-southeast-2 lambda -N -X POST https://xxxVous pouvez soit ajouter la fonction suivante à votre profil PowerShell, soit coller ce qui suit dans la même session PowerShell dans laquelle vous souhaitez exécuter la commande.
Fenêtre de terminal # PowerShell profile or current sessionfunction acurl {param([Parameter(Mandatory=$true)][string]$Region,[Parameter(Mandatory=$true)][string]$Service,[Parameter(ValueFromRemainingArguments=$true)][string[]]$CurlArgs)$AccessKey = aws configure get aws_access_key_id$SecretKey = aws configure get aws_secret_access_key$SessionToken = aws configure get aws_session_token& curl --aws-sigv4 "aws:amz:$Region`:$Service" --user "$AccessKey`:$SecretKey" -H "X-Amz-Security-Token: $SessionToken" @CurlArgs}Pour effectuer une requête curl authentifiée
sigv4, invoquezacurlen utilisant ces exemples :API Gateway
Section intitulée « API Gateway »Fenêtre de terminal acurl ap-southeast-2 execute-api -X GET https://xxxURL de fonction Lambda en streaming
Section intitulée « URL de fonction Lambda en streaming »Fenêtre de terminal acurl ap-southeast-2 lambda -N -X POST https://xxx
Pour démarrer votre serveur game-api local, exécutez la commande suivante :
TABLE_NAME=dungeon-adventure-infra-sandbox-Application-ElectroDbTableXXX-YYY pnpm nx run @dungeon-adventure/game-api:serveTABLE_NAME=dungeon-adventure-infra-sandbox-Application-ElectroDbTableXXX-YYY yarn nx run @dungeon-adventure/game-api:serveTABLE_NAME=dungeon-adventure-infra-sandbox-Application-ElectroDbTableXXX-YYY npx nx run @dungeon-adventure/game-api:serveTABLE_NAME=dungeon-adventure-infra-sandbox-Application-ElectroDbTableXXX-YYY bunx nx run @dungeon-adventure/game-api:serveUne fois votre serveur démarré, vous pouvez l’appeler en exécutant la commande suivante :
curl -X GET 'http://localhost:2022/games.query?input=%7B%7D'acurl ap-southeast-2 execute-api -X GET 'https://xxx.execute-api.ap-southeast-2.amazonaws.com/prod/games.query?input=%7B%7D'Si la commande s’exécute avec succès, vous verrez une réponse comme suit :
{"result":{"data":{"items":[],"cursor":null}}}Félicitations, vous avez construit et déployé votre première API avec tRPC ! 🎉🎉🎉