DEPRECATION NOTICE
This blueprint will be deprecated and eventually removed from this GitHub repository on October 27, 2024. No bugs will be fixed, and no new features will be added. The decision to deprecate is based on the lack of demand and interest in this blueprint, as well as the difficulty in allocating resources to maintain a blueprint that is not actively used by any users or customers.
If you are using this blueprint in production, please add yourself to the adopters.md page and raise an issue in the repository. This will help us reconsider and possibly retain and continue to maintain the blueprint. Otherwise, you can make a local copy or use existing tags to access it.
EMR on EKS with CDK blueprint
Introduction
In this post, we will learn how to use EMR on EKS AddOn and Teams in the cdk-eks-blueprints to deploy a an infrasturcture on EKS to submit Spark Job. The cdk-eks-blueprints allows you deploy an EKS cluster and enable it to be used by EMR on EKS service with minimal setup. The architecture below shows a conceptual view of the infrastructure you will deploy through this blueprint.
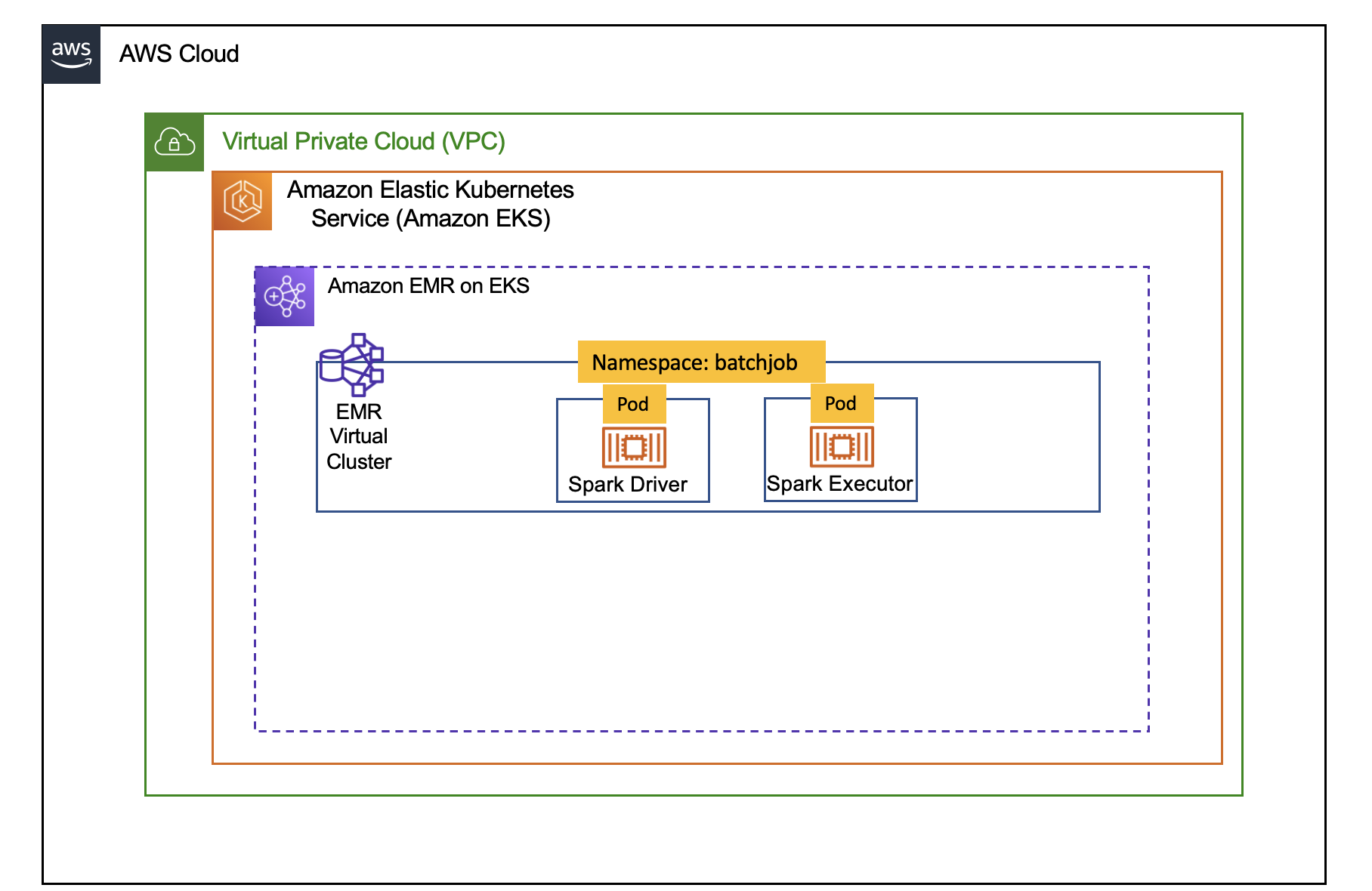
Deploying the Solution
In this example, you will provision the following:
- Creates EKS Cluster Control plane with public endpoint (for demo purpose only)
- Two managed node groups
- Core Node group with 3 AZs for running system critical pods. e.g., Cluster Autoscaler, CoreDNS, Logging etc.
- Spark Node group with single AZ for running Spark jobs
- Enable EMR on EKS and create one Data teams (
emr-data-team-a)- Creates new namespace for each team
- Creates Kubernetes role and role binding(
emr-containersuser) for the above namespace - New IAM role for the team execution role
- Update AWS_AUTH config map with emr-containers user and AWSServiceRoleForAmazonEMRContainers role
- Create a trust relationship between the job execution role and the identity of the EMR managed service account
- EMR Virtual Cluster for
emr-data-team-a - IAM policy for
emr-data-team-a - Deploys the following Kubernetes Add-ons
- Managed Add-ons
- VPC CNI, CoreDNS, KubeProxy, AWS EBS CSi Driver
- Self Managed Add-ons
- Metrics server with HA, Cluster Autoscaler, CertManager and AwsLoadBalancerController
- Managed Add-ons
This blueprint can also take an EKS cluster that you defined using the cdk-blueprints-library.
Prerequisites
Ensure that you have installed the following tools on your machine.
NOTE: You need to have an AWS account and region that are bootstrapped by AWS CDK.
Customize
The the entry point for this cdk blueprint is /bin/emr-eks.ts which instantiate a stack defined in lib/emr-eks-blueprint-stack.ts. This stack must be provided with a VPC and a list of EMR on EKS team definition and the role that will be admin of the EKS cluster. It can also take as options an EKS cluster defined through cdk-blueprints-library and the EKS cluster name.
The properties that are passed to the emr on eks blueprint stack are defined as such:
export interface EmrEksBlueprintProps extends StackProps {
clusterVpc: IVpc,
clusterAdminRoleArn: ArnPrincipal
dataTeams: EmrEksTeamProps[],
eksClusterName?: string, //Default eksBlueprintCluster
eksCluster?: GenericClusterProvider,
}
In this example we define a VPC in lib/vpc.ts and is instantiated in bin/emr-eks.ts. We also define a team called emr-data-team-a and which has an execution role called myBlueprintExecRole.
The blueprint will deploy by default an EKS cluster with the managed nodegroups defined in the section Deploying the Solution.
Deploy
Before you run the solution, you MUST change the clusterAdminRoleArn of the props object in lib/emr-eks.ts. This role allows you to interact manage EKS cluster and should have be allowed at least the IAM action eks:AccessKubernetesApi.
Clone the repository
git clone https://github.com/awslabs/data-on-eks.git
Navigate into one of the example directories and run cdk synth
cd analytics/cdk/emr-eks
npm install
cdk synth --profile YOUR-AWS-PROFILE
Deploy the pattern
cdk deploy --all
Enter yes to deploy.
Verify the resources
Let’s verify the resources created by cdk deploy.
Verify the Amazon EKS Cluster
aws eks describe-cluster --name eksBlueprintCluster # Update the name cluster name if you supplied your own
Verify EMR on EKS Namespaces batchjob and Pod status for Metrics Server and Cluster Autoscaler.
aws eks --region <ENTER_YOUR_REGION> update-kubeconfig --name eksBlueprintCluster # Creates k8s config file to authenticate with EKS Cluster. Update the name cluster name if you supplied your own
kubectl get nodes # Output shows the EKS Managed Node group nodes
kubectl get ns | grep batchjob # Output shows batchjob
kubectl get pods --namespace=kube-system | grep metrics-server # Output shows Metric Server pod
kubectl get pods --namespace=kube-system | grep cluster-autoscaler # Output shows Cluster Autoscaler pod
Execute Sample Spark job on EMR Virtual Cluster
Execute the Spark job using the below shell script.
- Once you deploy the blueprint you will have as output the Virtual Cluster id. You can use the id and the execution role for which you supplied a policy to submit jobs. Below you can find an example of a job you can submit with AWS CLI.
export EMR_ROLE_ARN=arn:aws:iam::<YOUR-ACCOUNT-ID>:role/myBlueprintExecRole
aws emr-containers start-job-run \
--virtual-cluster-id=<VIRTUAL-CLUSTER-ID-IN-CDK-OUTPUT> \
--name=pi-2 \
--execution-role-arn=$EMR_ROLE_ARN \
--release-label=emr-6.8.0-latest \
--job-driver='{
"sparkSubmitJobDriver": {
"entryPoint": "local:///usr/lib/spark/examples/src/main/python/pi.py",
"sparkSubmitParameters": "--conf spark.executor.instances=1 --conf spark.executor.memory=2G --conf spark.executor.cores=1 --conf spark.driver.cores=1 --conf spark.kubernetes.node.selector.app=spark"
}
}'
Verify the job execution
kubectl get pods --namespace=batchjob -w
Cleanup
To clean up your environment, you call the command below. This will destroy the Kubernetes Add-ons, EKS cluster with Node groups and VPC
cdk destroy --all
To avoid unwanted charges to your AWS account, delete all the AWS resources created during this deployment