KeyBERT
This middleware is based on the KeyBERT keyword extraction and topic modeling library. It leverages the power of embedding models to identify the most significant keywords and topics in a text document, and to enrich the document metadata with them.
🏷️ Keyword Extraction
To use this middleware, you import it in your CDK stack and connect it to a data source that provides text documents, such as the S3 Trigger if your text documents are stored in S3.
import { KeybertTextProcessor } from '@project-lakechain/keybert-text-processor';import { CacheStorage } from '@project-lakechain/core';
class Stack extends cdk.Stack { constructor(scope: cdk.Construct, id: string) { // Sample VPC. const vpc = new ec2.Vpc(this, 'VPC', {});
// The cache storage. const cache = new CacheStorage(this, 'Cache');
// Create the KeyBERT text processor. const keybert = new KeybertTextProcessor.Builder() .withScope(this) .withIdentifier('Keybert') .withCacheStorage(cache) .withSource(source) // 👈 Specify a data source .withVpc(vpc) .build(); }}Embedding Model
It is possible to customize the embedding model that KeyBERT is going to use to analyze input documents.
ℹ️ At this time, only models from the Sentence Transformers library are supported.
import { KeybertTextProcessor, KeybertEmbeddingModel } from '@project-lakechain/keybert-text-processor';
const keybert = new KeybertTextProcessor.Builder() .withScope(this) .withIdentifier('Keybert') .withCacheStorage(cache) .withSource(trigger) .withVpc(vpc) .withEmbeddingModel( KeybertEmbeddingModel.ALL_MPNET_BASE_V2 ) .build();Options
There are different options influencing how the KeyBERT library extracts topics from input documents that you can optionally customize.
const keybert = new KeybertTextProcessor.Builder() .withScope(this) .withIdentifier('Keybert') .withCacheStorage(cache) .withSource(trigger) .withVpc(vpc) // The maximum number of keywords to extract. .withTopN(5) // Sets whether to use the max sum algorithm. .withUseMaxSum(false) // Sets the diversity of the results between 0 and 1. .withDiversity(0.5) // Sets the number of candidates to consider if `useMaxSum` is // et to `true`. .withCandidates(20) .build();📄 Output
The KeyBERT text processor middleware does not modify or alter source documents in any way. It instead enriches the metadata of documents with a collection of topics extracted from their text.
💁 Click to expand example
{ "specversion": "1.0", "id": "1780d5de-fd6f-4530-98d7-82ebee85ea39", "type": "document-created", "time": "2023-10-22T13:19:10.657Z", "data": { "chainId": "6ebf76e4-f70c-440c-98f9-3e3e7eb34c79", "source": { "url": "s3://bucket/text.txt", "type": "text/plain", "size": 24532, "etag": "1243cbd6cf145453c8b5519a2ada4779" }, "document": { "url": "s3://bucket/text.txt", "type": "text/plain", "size": 24532, "etag": "1243cbd6cf145453c8b5519a2ada4779" }, "metadata": { "keywords": ["ai", "machine learning", "nlp"] }, "callStack": [] }}🏗️ Architecture
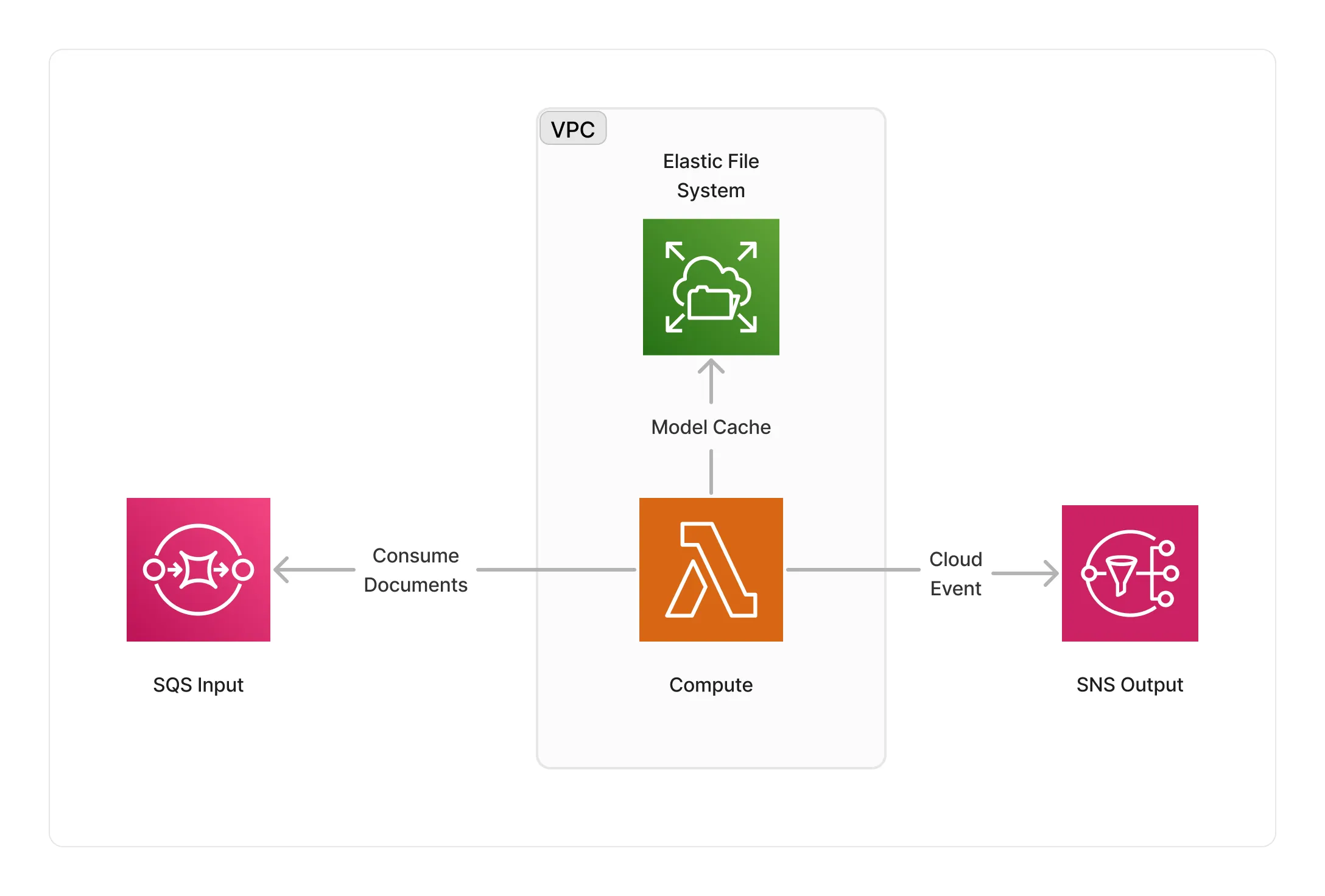
The KeyBERT middleware runs within a Lambda compute running the KeyBERT library packaged as a Docker container. The Lambda compute runs within a VPC, and caches KeyBERT embedding models on an EFS storage.
🏷️ Properties
Supported Inputs
| Mime Type | Description |
|---|---|
text/plain | UTF-8 text documents. |
Supported Outputs
| Mime Type | Description |
|---|---|
text/plain | UTF-8 text documents. |
Supported Compute Types
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
CPU | This middleware only supports CPU compute. |
📖 Examples
- Topic Modeling Pipeline - An example showcasing how to extract relevant topics from text documents.