NLP
The NLP text processor middleware uses Amazon Comprehend to provide natural language processing capabilities to your pipelines. It allows you to analyze and extract the substance of text documents and use that as an input to other middlewares in your pipeline. For example, running sentiment analysis, PII detection, part-of-speech tagging, and named entity recognition on your text documents.
💡 Intents
To use this middleware, you define an intent that specifies the type of processing you want to operate on text. Intents expose a powerful functional API making it easy to describe the processing you want to leverage when processing text documents.
In the following sections, we will explore several use-cases that demonstrate how to use intents.
Language Detection
Let’s start with a simple example where we use Amazon Comprehend’s ability to detect the language of text documents. In the below example, we define an intent that will extract language information from text documents and store it within the document metadata.
💁 We’re using the intent domain-specific language (DSL) to express actions within an intent.
import { NlpTextProcessor, dsl as l } from '@project-lakechain/nlp-text-processor';import { CacheStorage } from '@project-lakechain/core';
class Stack extends cdk.Stack { constructor(scope: cdk.Construct, id: string) { const cache = new CacheStorage(this, 'Cache');
// Create the NLP text processor. const nlpProcessor = new NlpTextProcessor.Builder() .withScope(this) .withIdentifier('TextProcessor') .withCacheStorage(cache) .withSource(source) .withIntent( l.nlp().language() // 👈 Intent ) .build(); }}Sentiment Analysis
Amazon Comprehend can also be used to perform sentiment analysis on text documents.
💁 We’re using the
languageintent action before thesentimentaction as the sentiment action needs to know the language of the document first. We’re doing this by chaining both actions together.
const nlpProcessor = new NlpTextProcessor.Builder() .withScope(this) .withIdentifier('TextProcessor') .withCacheStorage(cache) .withSource(source) .withIntent( l.nlp().language().sentiment() // 👈 Intent ) .build();PII Detection
Amazon Comprehend can identify personally identifiable information (PII) entities in text documents. You can enable PII detection using the NLP text processor by using the pii intent action.
💁 We’re using the
languageintent action before thepiiaction as the PII action needs to know the language of the document first. We’re doing this by chaining both actions together.
const nlpProcessor = new NlpTextProcessor.Builder() .withScope(this) .withIdentifier('TextProcessor') .withCacheStorage(cache) .withSource(source) .withIntent( l.nlp().language().pii() // 👈 Intent ) .build();Part-of-Speech Tagging
Leveraging Comprehend’s ability to perform part-of-speech tagging on text documents is as simple as using the pos intent action. POS tagging identifies the grammatical parts of speech in a sentence, such as verbs, nouns, adjectives, adverbs, etc.
💁 We’re using the
languageintent action before theposaction as the POS action needs to know the language of the document first. We’re doing this by chaining both actions together.
const nlpProcessor = new NlpTextProcessor.Builder() .withScope(this) .withIdentifier('TextProcessor') .withCacheStorage(cache) .withSource(source) .withIntent( l.nlp().language().pos() // 👈 Intent ) .build();Entity Recognition
To use Amazon Comprehend’s ability to recognize entities, such as events, locations, dates, and more, within your text documents, you can use the entities intent action.
💁 We’re using the
languageintent action before theentitiesaction as the entities action needs to know the language of the document first. We’re doing this by chaining both actions together.
const nlpProcessor = new NlpTextProcessor.Builder() .withScope(this) .withIdentifier('TextProcessor') .withCacheStorage(cache) .withSource(source) .withIntent( l.nlp().language().entities() // 👈 Intent ) .build();Reading Time
You can use the readingTime intent action to calculate the estimated reading time of a text document. The estimated reading time will be stored within the document metadata.
const nlpProcessor = new NlpTextProcessor.Builder() .withScope(this) .withIdentifier('TextProcessor') .withCacheStorage(cache) .withSource(source) .withIntent( l.nlp().readingTime() // 👈 Intent ) .build();Statistics
To extract other statistics from text documents, such as the count of the number of sentences and words in the document, you can use the stats intent action.
const nlpProcessor = new NlpTextProcessor.Builder() .withScope(this) .withIdentifier('TextProcessor') .withCacheStorage(cache) .withSource(source) .withIntent( l.nlp().stats() // 👈 Intent ) .build();Combining Actions
All actions can be combined within a single intent, and the NLP text processor will execute them in the order in which they are defined.
const nlpProcessor = new NlpTextProcessor.Builder() .withScope(this) .withIdentifier('TextProcessor') .withCacheStorage(cache) .withSource(source) .withIntent( l.nlp() .language() .sentiment() .pii() .entities() .readingTime() .sentences() ) .build();📑 Using Filters
Each action within the DSL supports one or more filters that you can apply to it. For example, the pii, entities, and pos actions support different filters.
💁 The below intent extracts PII with 90% or more confidence, entities associated with
PEOPLEtags, and part-of-speech tags associated with adjectives and nouns with 90% or more confidence.
const nlpProcessor = new NlpTextProcessor.Builder() .withScope(this) .withIdentifier('TextProcessor') .withCacheStorage(cache) .withSource(source) .withIntent( l.nlp() .language() .pii(l.confidence(0.9)) .entities(l.filter('PERSON')) .pos(l.confidence(0.9), l.filter('ADJ', 'NOUN')) ) .build();🏗️ Architecture
The NLP text processor uses AWS Lambda as its compute, using an ARM64 architecture. The Lambda function is integrated with the Amazon Comprehend service, and issues the appropriate API calls to process images given the intent defined by the user.
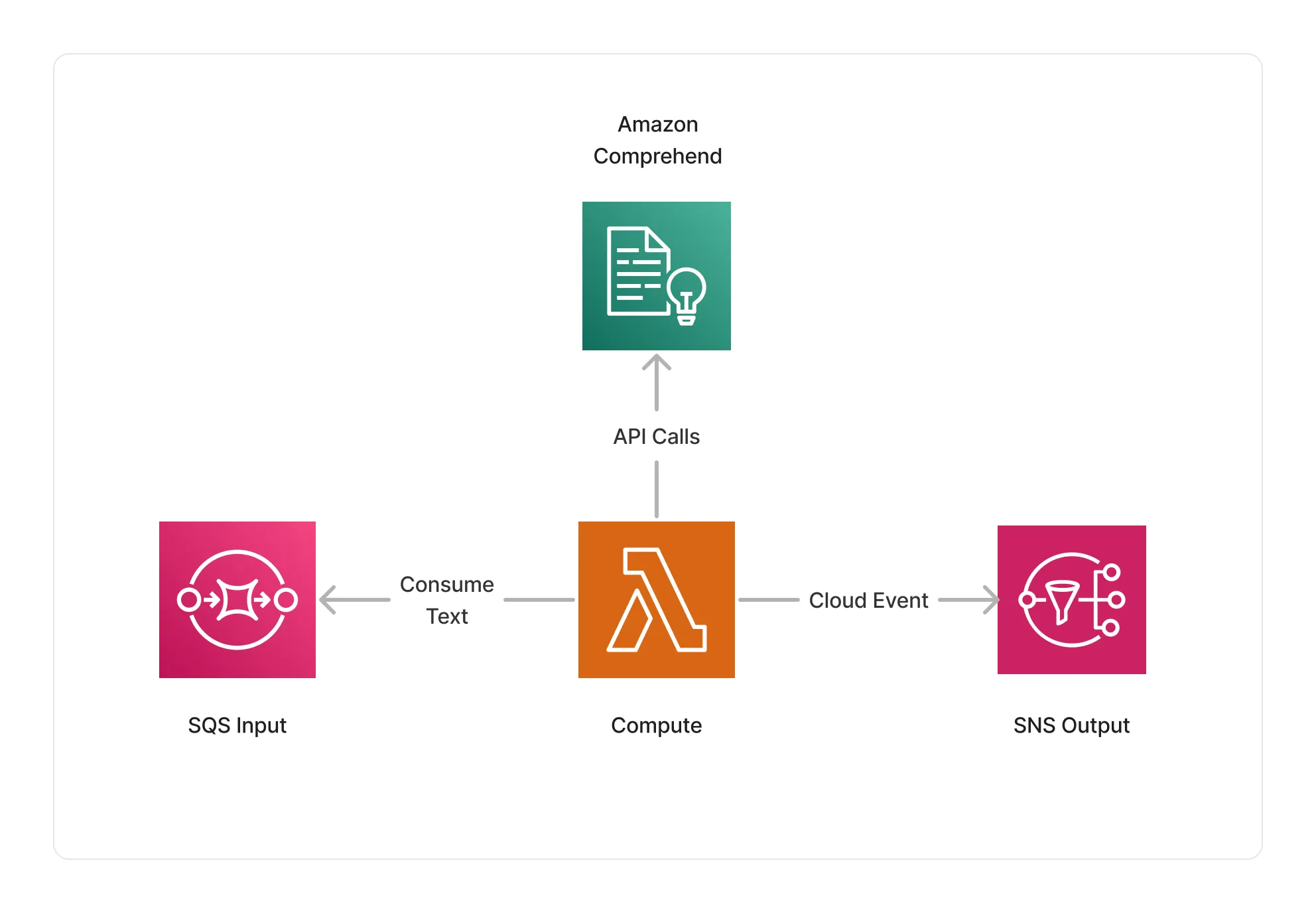
🏷️ Properties
Supported Inputs
| Mime Type | Description |
|---|---|
text/plain | This middleware supports plain text as input. |
Supported Outputs
| Mime Type | Description |
|---|---|
text/plain | This middleware supports plain text as output. |
Supported Compute Types
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
CPU | This middleware only supports CPU compute. |
📖 Examples
- NLP Pipeline - Builds a pipeline for extracting metadata from text-oriented documents.
- PII Redaction Pipeline - A PII redaction pipeline using Project Lakechain.